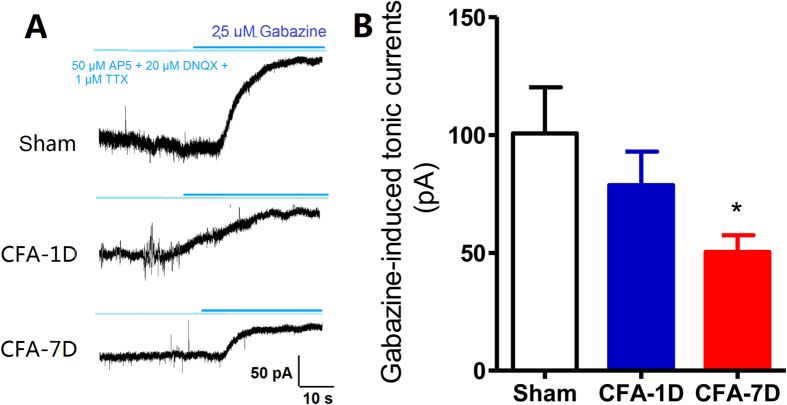
Figure 2. Decreased tonic inhibition of extra-synaptic GABAARs in the VB in CFA-induced chronic inflammatory pain rats (CFA-7D).
Representative traces of tonic inhibition recordings from thalamic relay neurons in the control (n = 8 cells), CFA-1D (n = 10 cells) and CFA-7D (n = 10 cells) groups after inhibiting ionotropic glutamatergic components (AP5 50 μM, DNQX 20 μM) and sodium currents (TTX 1 μM). Gabazine (25 μM), a competitive GABAARs antagonist, produced a positive shift and blocked both phasic and tonic currents. (B) Maximal current changes after gabazine (25 μM) application measured as the shift of GABAergic tonic inhibition (∆IPSCtonic = IPSCafter − IPSCbefore). The histogram of tonic inhibitory currents showed a reduction of tonic inhibitory currents in the CFA-7D, but not the CFA-1D groups. Error bars indicated SEMs, *P < 0.05 compared with the control group, one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test.