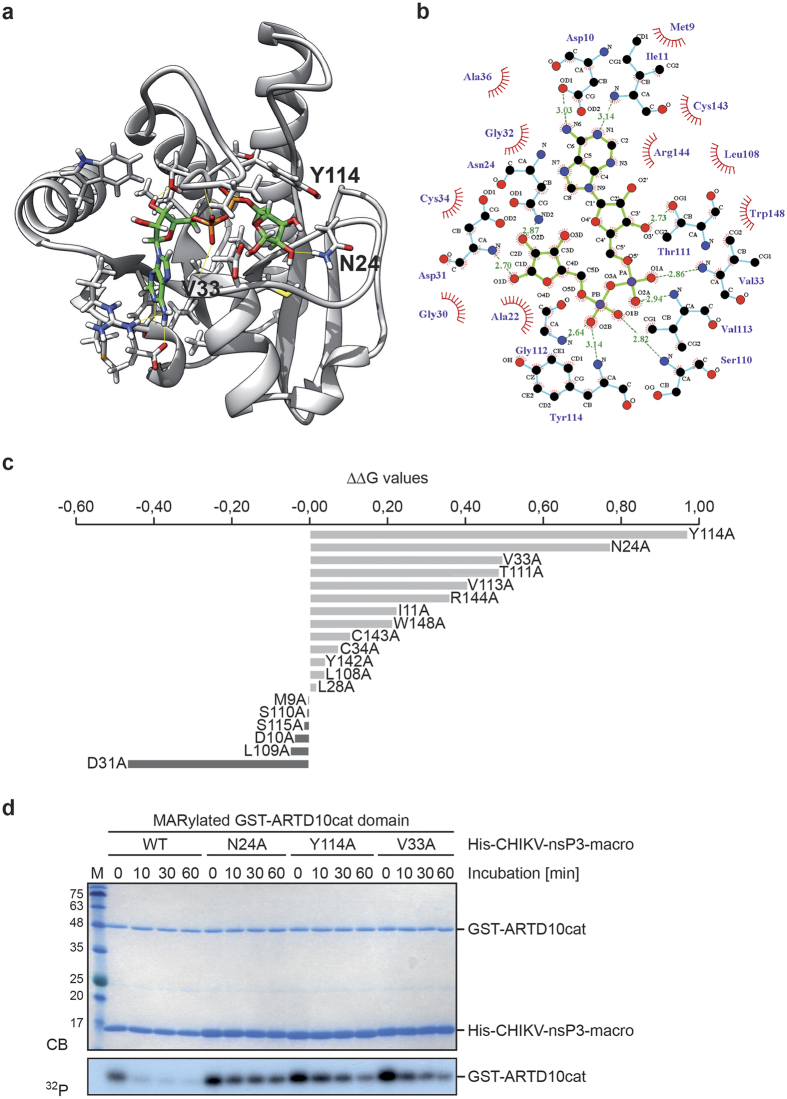
Figure 5. Identification of amino acids in the CHIKV macrodomain that are important for catalysis.
(a) Structural model of the CHIKV macrodomain derived from the crystal structure (PDBID 3GPO). Highlighted are the amino acids that are relevant for ADPr binding and thus important for catalytic activity. The protein is in grey cartoon representation. ADPr and the binding site residues involved in ligand coordination are depicted in green and grey licorice, respectively. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as yellow lines. (b) 2D representation of ADPr in complex with the CHIKV macrodomain is shown based on the LIGPLOT program. ADPr is shown in green lines. Hydrophobic contacts are represented by an arc with spokes radiating towards the ligand atoms they contact. The contacted atoms are shown with spokes radiating back. The carbon atoms, oxygen atoms, and nitrogen atoms are colored in black, red and blue, respectively. The hydrogen bonds that are defined by the crystal structure (panel a) of CHIKV-nsP3-macro with ADPr are depicted in green dashed lines. (c) In silico alanine scan and ΔΔG values for ADPr binding. Mutation of Y114, N24, and V33 to alanine showed the highest potential effect on ADPr binding. (d) CHIKV macrodomain mutants with N24A, V33A and Y114A were expressed as His6-tagged fusion proteins in bacteria. Then the purified proteins were incubated with automodified GST-ARTD10cat domain for the indicated times. The proteins were visualized by Coomassie blue staining (CB) and de-MARylation activity of CHIKV macrodomain mutants was determined by autoradiography (32P). CB, Coomassie blue; 32P, autoradiography.