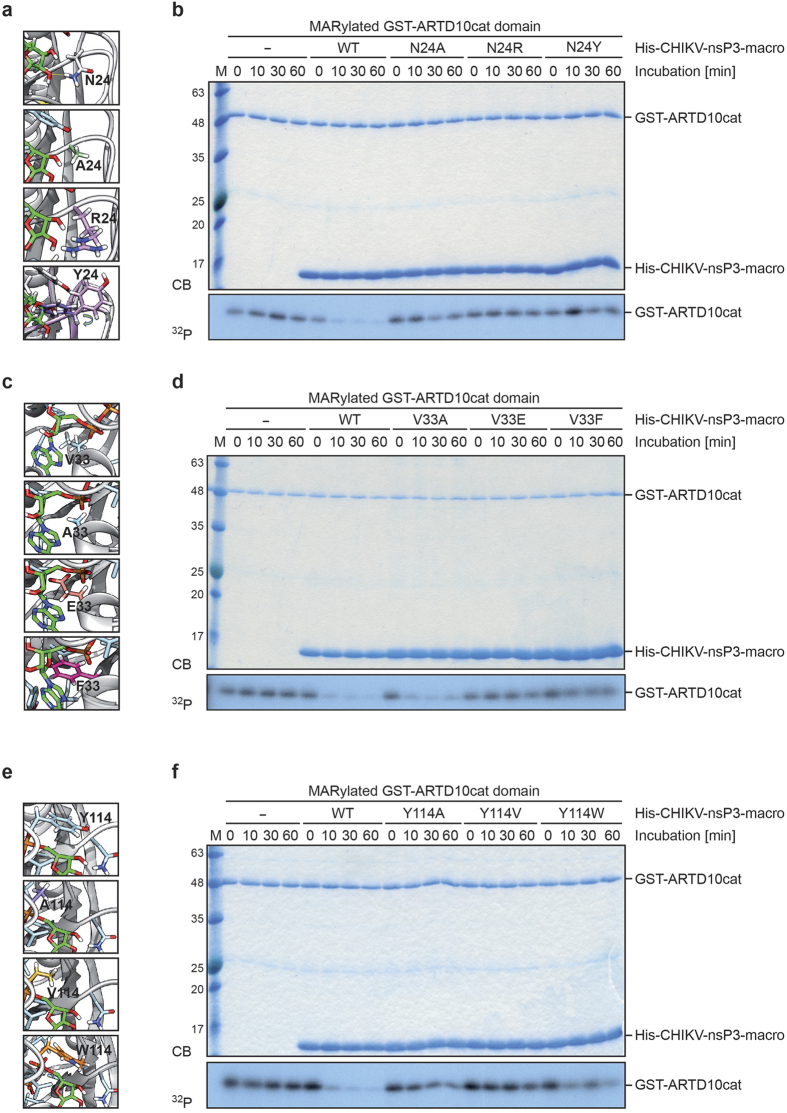
Figure 6. Identification of CHIKV macrodomain mutants that are catalytically inactive.
(a) Focus on amino acid N24 of the structural model of the CHIKV macrodomain. The models of the mutants obtained by substitutions of position 24 with alanine, arginine and tyrosine are shown. The protein is in grey cartoon representation, while the ADPr is in green licorice representation. (b) CHIKV macrodomain mutants with N24R and N24Y, both having a higher Amber score than N24A, were expressed as His6-tagged fusion proteins in bacteria. Mutant proteins were evaluated by incubation with automodified GST-ARTD10cat domain for the indicated times. Proteins were visualized by Coomassie blue (CB) staining and the activities of the CHIKV macrodomain mutants were determined by autoradiography (32P). (c) Focus on amino acid V33 of the structural model of the CHIKV macrodomain. The models of the mutants obtained by substitutions of position 33 with alanine, glutamate and phenylalanine are shown. Coloring is as in panel a. (d) CHIKV macrodomain mutants with V33E and V33F, both having a higher Amber score than V33A, were expressed as His6-tagged fusion proteins in bacteria. Mutants were analyzed as described in panel b. (e) Focus on amino acid Y114 of the structural model of the CHIKV macrodomain. The models of the mutants obtained by substitution of position 114 with alanine, valine and tryptophan. Coloring is as in panel a. (f) CHIKV macrodomain mutants with Y114V and Y114W, both having a higher Amber score than Y114A, were expressed as His6-tagged fusion proteins in bacteria. Mutants were analyzed as described in panel b. CB, Coomassie blue; 32P, autoradiogram.