Figure 2.
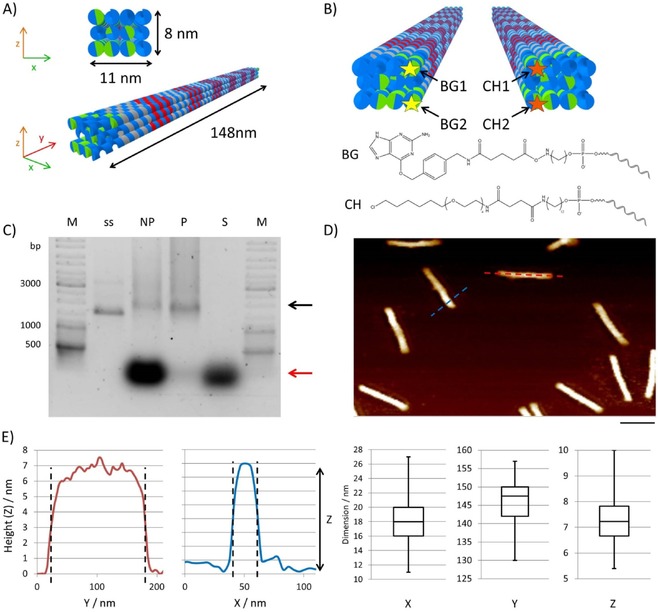
Design and analysis of DNA origami nanostructures. A) Schematic representation of the 3D DON‐1 design. B) Position (top) and chemical structure (bottom) of the staple strands used for the incorporation of the suicide ligands benzylguanine (BG) and chlorohexane (CH) at 5 ’ ends of the selected staple oligonucleotides. C) Ethidium bromide‐stained 0.75 % agarose gel of DON samples before (not purified, NP) and after (purified, P) PEG purification. M: GeneRuler DNA Ladder Mix. The supernatant (S) removed after precipitation contains the non‐incorporated staple strands (red arrow). The assembled DONs are indicated by the black arrow; ss: single‐stranded scaffold. D) Representative AFM image of purified DON‐1, indicating monodispersed rod‐shaped particles. Scale bar: 100 nm. E) Height profiles obtained from AFM images along the cross‐sections are marked in blue and red in panel (D). The box‐whisker plots show the results of the statistical analysis of 60 particles to determine their dimensions along their axes. The values for x and y were determined from the cross‐sections, whereas the z values were determined from the particle's heights.
