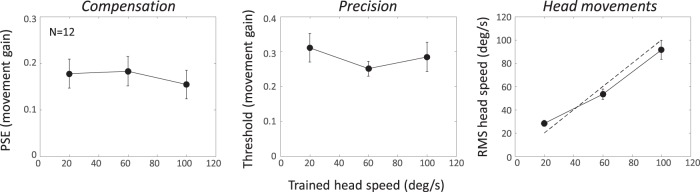
Figure 4.
The left panel shows the mean ability to compensate as a function of the trained head speed for 12 listeners. The movement gain is small and positive, indicating good if incomplete compensation. Hence, a stationary sound appears to move slightly against the head movement (in vision, this is called the Filehne illusion); to cancel the perceived motion requires a small amount of source movement in the same direction as the head rotation. The middle panel shows the mean threshold or slope of the psychometric function. The results show that precision of compensation does not vary across a wide range of head speeds. The right panel plots the mean root mean square head speed obtained in the main experiment, with the dotted line indicating ideal reproduction of the trained head speeds. All error bars are ±1 SE. PSE = point of subjective equality.