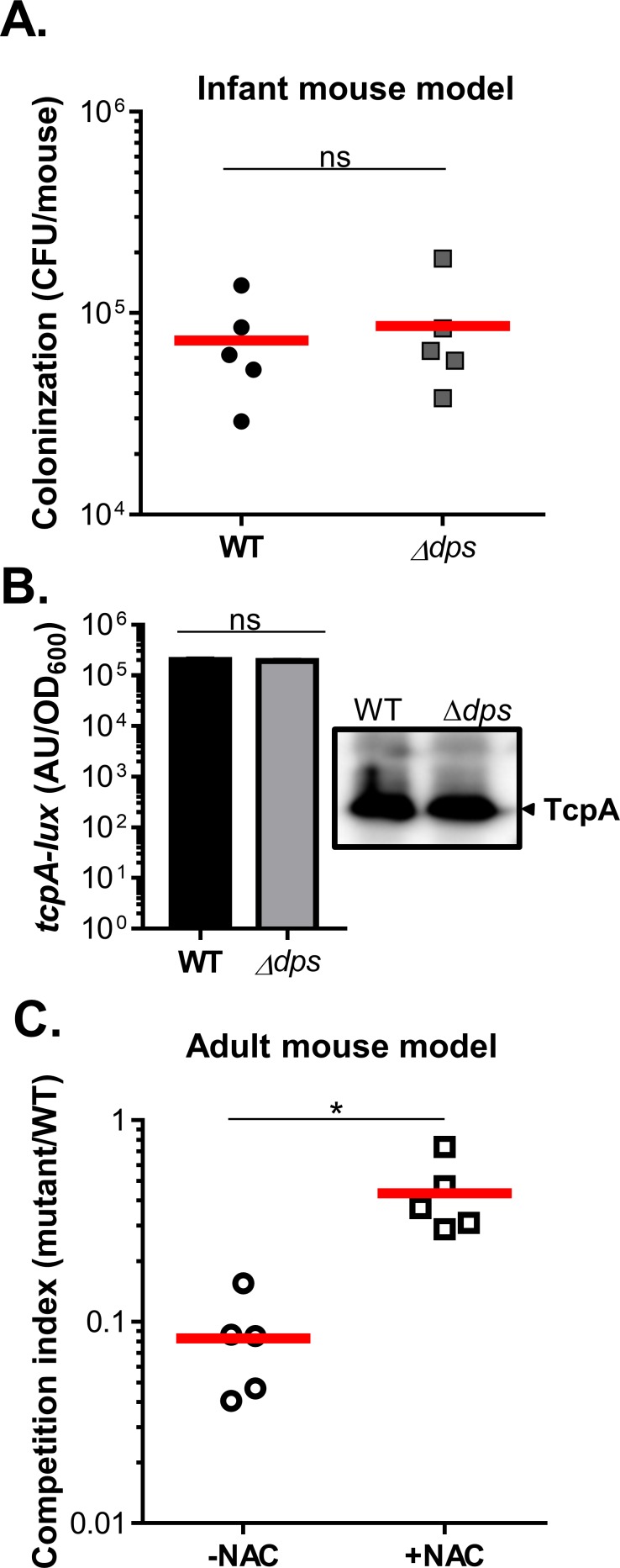
Fig 6. The effect of Dps on V. cholerae pathogenesis.
A. Infant mouse colonization: Approximately 105 wild type (lacZ-) and dps mutants (lacZ+) were intragastrically inoculated into 5-day-old CD-1 mice in a 1:1 ratio. After 18-hr incubation, CFU from small intestines were determined by serial dilution and plated on LB agar. The data shown are from three independent experiments and each symbol represents CFU recovered from one mouse intestine. Horizontal lines represent the average number of cells recovered. B. Virulence factor expression and production: wild type and Δdps containing PtcpA-luxCDABE were grown under the virulence inducing AKI condition [37]. Luminescence was measured and normalized to OD600 (left panel), and 109 cells were subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotting using anti-TcpA antiserum (right panel). C. Colonization in adult mice: Five-week-old CD-1 mice were provided with drinking water with or without the antioxidant NAC for one week. Mice were then treated with streptomycin and intragastrically administered a 1:1 mixture of wild type (lacZ-) and Δdps (lacZ+). Fecal pellets were collected from each mouse at the indicated time points, resuspended in PBS, serially diluted, and then plated on plates containing X-gal. The competitive index (CI) was calculated as the ratio of mutant to wild type colonies normalized to the input ratio. Horizontal lines represent the average CI. *: P<0.05.