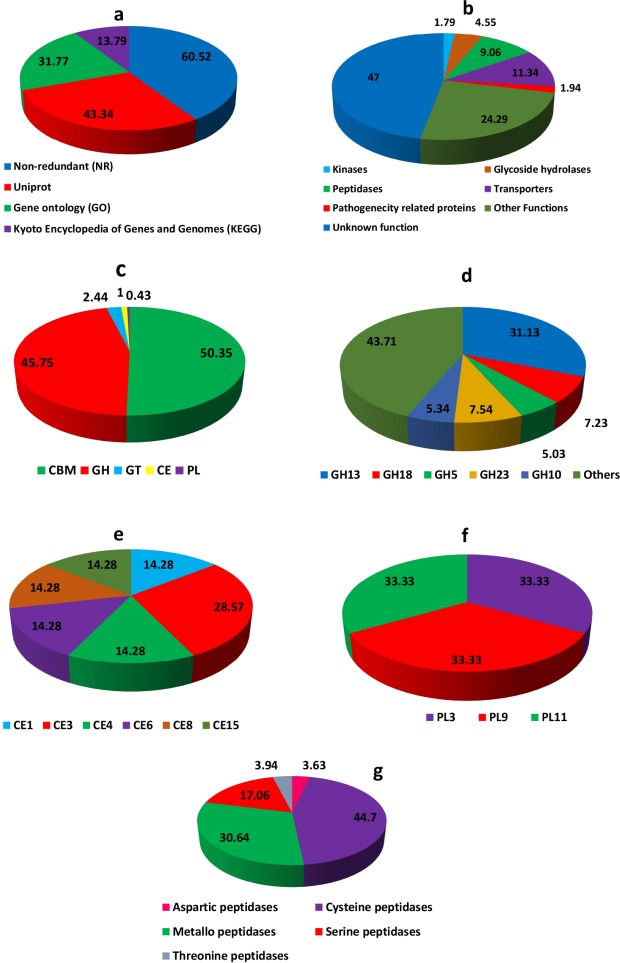
Fig 2.
Functional annotation of the T. indica effector candidates (a) Gene annotation of predicted genes using NCBI non-redundant (NR), Uniprot, Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) databases. (b) Percentage distribution of the proteins with distinct enzymatic functions. (c) Summary of the CAZyme categories: carbohydrate-binding modules (CBMs), carbohydrate esterases (CEs), glucoside hydrolases (GHs), glycosyl transferases (GTs), polysaccharide lyases (PLs). (d) Percent distributon of most abundant Glycosyl hydrolases (GH). (e) Percent distributon of most abundant carbohydrate esterases (CEs). (f) Percent distributon of most abundant of most abundant polysaccharide lyases (PLs). The prediction of CAZymes from T. indica effector candidates and their classification were performed using tools from the Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes (CAZyme) database. (g) Percentage distribution of different types of peptidases present in T. indica genome.