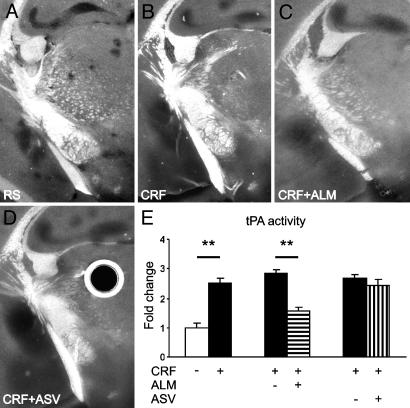
Fig. 2.
CRF increases tPA activity in the amygdala in brain slices by means of the CRF-R1 receptor. CRF caused a significant up-regulation of tPA in the central and medial amygdala in comparison with the slice perfused with RS only (dark lytic areas in B vs. A). This up-regulation was inhibited by the CRF-R1 antagonist, antalarmin (ALM, C), but not the CRF-R2 antagonist Antisauvagine 30 (ASV, D). Slices perfused with CRF with addition of ALM or ASV vehicle (corresponding to C and D) are not shown. Round dark area with bright halo in D is an artifact caused by an air bubble in the overlay gel. (E) Quantification of changes shown in A-D (n = 5 slices per group) in relation to the mean area of lysis in slices perfused with RS only. **, P < 0.05.