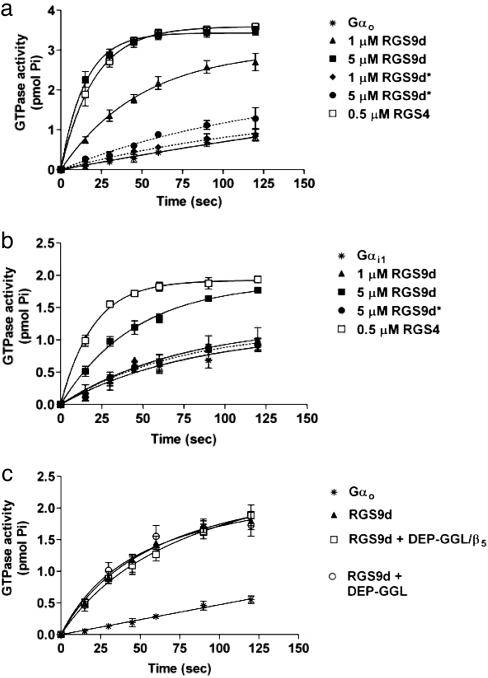
Fig. 4.
RGS9 stimulates the intrinsic GTPase activity of Gαo and Gαi1 in a single-turnover assay. (a) RGS9d accelerates Go GTPase activity (intrinsic rate constant k = 0.002 min-1) in a concentration-dependent manner (1 μM RGS9d, k = 0.021; 5 μM RGS9d, k = 0.067 min-1). Introduction of the point mutation I363T within the RGS domain near a critical Gi1 contact site (RGS9d*) eliminates the GTPase activity of this construct (1 μM RGS9d, k = 0.003; 5 μM RGS9d, k = 0.007 min-1). (b) RGS9d accelerates Gi1 GTPase activity (intrinsic rate constant k = 0.01 min-1) with lower potency than that observed for Gαo. Also similar to Gαo, RGS9d* is devoid of GAP activity toward Gαi1 (5 μM RGS9d*, k = 0.012; 1 μM RGS9d, k = 0.014; 5 μM RGS9d, k = 0.022 min-1). (c) Neither DEP-GGL nor DEP-GGL/Gβ5 directly influences the GAP activity of RGS9d toward Gαo. Neither construct affects the GTPase activity of Gαo in the absence of RGS9d.