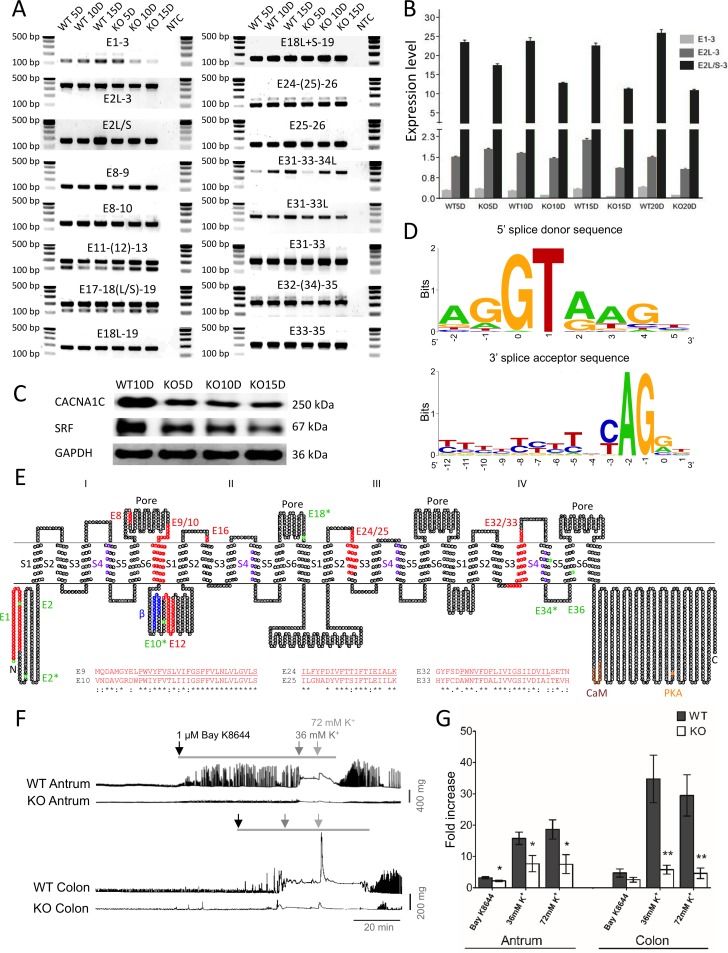
Fig 6. Alternations of L-type calcium channel transcripts, protein, and action potential in KO smooth muscle.
(A) PCR validation of alternatively started and spliced exons of Cacna1c in WT and KO jejunum smooth muscle at KO days 5, 10, and 15. NTC is non template control. Primer sets were designed from variant exons in the regions (e.g. E1-3, forward primer spanning a region on exon 1 and reverse primer on exon 3). (B) qPCR data showing decreased expression of Cacna1c variants starting at exon 1 and exon 2 long and short forms (E1-3, E2L-3, and E2L/S-3) at KO days 5, 10, 15, and 20. E1-3, a region spanning exons 1 and 3; E2L-3, a region spanning exon 2 long (L) form and exon 3; E2L/S-3, a region spanning exon 2 long (L) and short (S) forms and exon 3. (C) Western blot showing decreased levels of CACNA1C protein in Srf KO muscle. (D) Consensus sequence of 5’ splice donor and 3’ splice acceptor sites. (E) A topological map of CACNA1C variants. Amino acid sequence is written in small circles. Four motifs are indicated as I-IV and six transmembrane domains, S1-S6. Four pore regions are also indicated. Colors on amino acid sequence show particular regions and domains: red, missing or inserted peptides from differentially spliced exons; purple, voltage sensors in S4 transmembrane domains; green, start codons found in differentially spliced variants (*, start codons deduced from indicated exons that are differentially spliced; blue, β subunit binding domain; brown, CaM (calmodulin) binding domain; orange, PKA (protein kinase A) phosphorylation site. Alignment of alternatively spliced exons E9/10, E24/25, and E32/33 are shown. (F) Isometric force recordings from antrum and colon of WT and KO mice. Bay K8644 (1 μM) and high potassium (K+) Krebs (36 mM and 72 mM) were applied to the tissues (indicated by bar and arrows). (G) The graph summarizes the results for 9 antral and 5 colonic WT and KO tissues. The responses to Bay K8644, 36 mM K+, and 72 mM K+ were significantly decreased in KO antrums, and the responses to 36 mM K+ and 72 mM K+ were significantly reduced in KO colons compared to WT. * and ** represent p ≤ 0.05 and p ≤ 0.01 respectively.