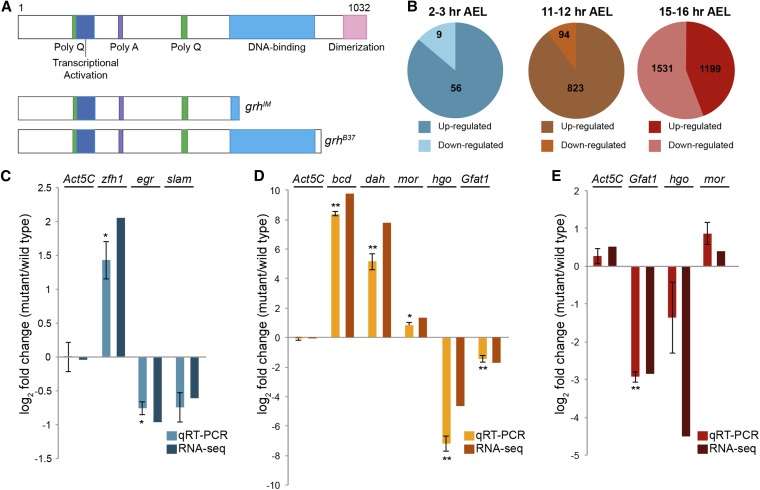
Figure 4.
Thousands of genes require Grh for expression. (A) The Grh polypeptide produced from the grh-RH isoform, and predicted peptides produced from grhIM and grhB37 mutants. DNA-binding and dimerization domains are shared among all grh splice isoforms. (B) Numbers of genes up or downregulated in grh mutants as determined by RNA-seq. Data from 2–3 hr embryos were generated by comparing embryos depleted of maternally provided grh to their heterozygous siblings. Data from 11–12 and 15–16 hr embryos were generated by comparing zygotic mutants homozygous for null mutants in grh to their heterozygous siblings. (C–E) Quantitative RT-PCR to assess gene expression levels in grhB37 mutant embryos as compared to wild type presented as log2 fold change (mutant/wild type). (C) 2–3 hr AEL. (D) 11–12 hr AEL. (E) 15–16 hr AEL. Error bars indicate the SEM for >3 biological replicates. *t-test P-value ≤0.05, **t-test P-value ≤0.005. t-test relative to Act5C control.