Figure 5.
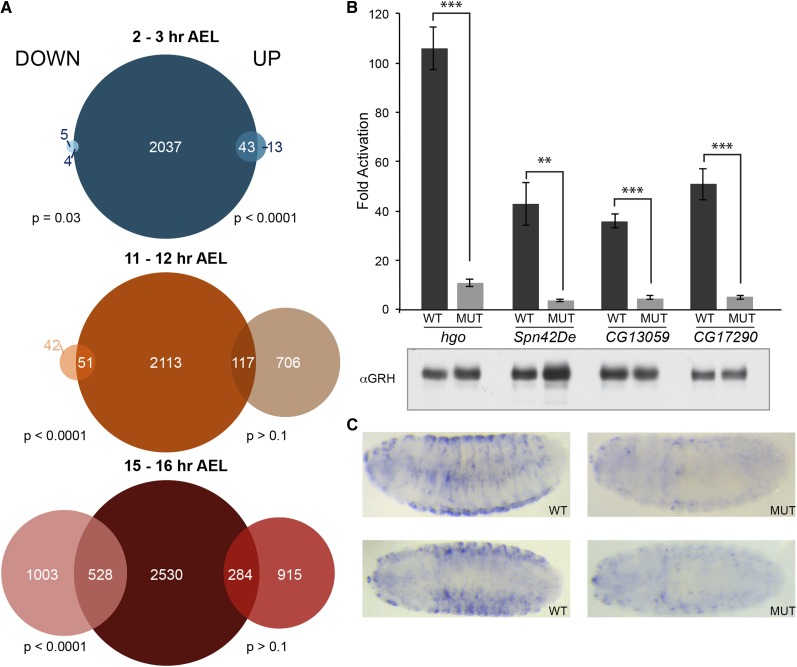
Grh transitions from a transcriptional repressor early in embryonic development to an activator and repressor later. (A) Venn diagrams for data from 2–3 hr embryos (top), 11–12 hr embryos (middle), and 15–16 hr embryos (bottom), depicting the overlap of genes downregulated (left) or upregulated (right) in the absence of Grh with genes associated with Grh-binding sites identified by ChIP-seq (center). (P-values calculated by Fisher’s exact test.) (B) Fold activation by Grh of firefly luciferase reporters driven by either wild-type (WT) promoters for hgo, Spn42De, CG13059, or CG17290, or promoters with mutations in the identified Grh-binding site (MUT). Error bars indicate SD (n = 3) ***t-test P-value <0.0002. **t-test P-value <0.002. Western blot showing Grh expression in representative assays (below). (C) In situ hybridizations against lacZ on transgenic embryos with either a wild-type hgo promoter driving lacZ (WT) or a promoter with a mutated Grh-binding site (MUT). Two examples are given for each.