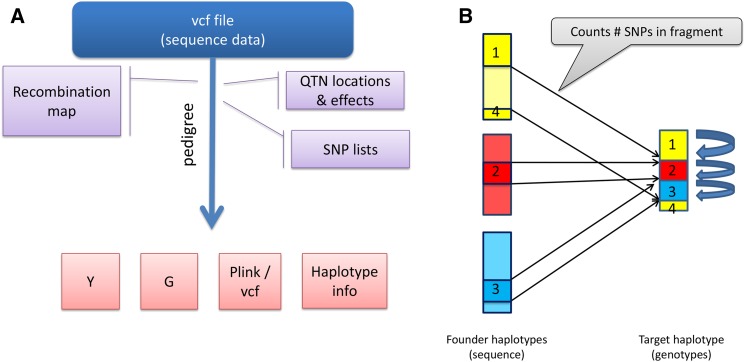
Figure 1.
General outline of SBVB. (A) As input, SBVB reads the vcf file containing all phased SNPs from founder haplotypes. Additional files specify the genetic architecture, the lists of SNPs (each corresponding to one array), and the recombination map for each sex and genome location (optional). SBVB then performs gene dropping following a predetermined pedigree, generating phenotypes (Y), genomic relationship matrices (G, one per SNP list), and molecular genotypes for each individual in a pedigree and for each SNP list in Plink or vcf format, and a file containing haplotype information that allows quick restart of the program. (B) SBVB represents each generated haplotype as a list of only recombination breakpoints and ids of founder haplotypes. In the figure, a hypothetical target haplotype contains four blocks, delimited by the three recombination breakpoints that have been transmitted from three founders, each with a different color. When needed, the genotypes of the target haplotype can be quickly recovered simply by counting how many SNPs are between each recombination event and knowing the founder id of each block. id, identity; QTN, quantitative trait nucleotide; SBVB, sequence-based virtual breeding.