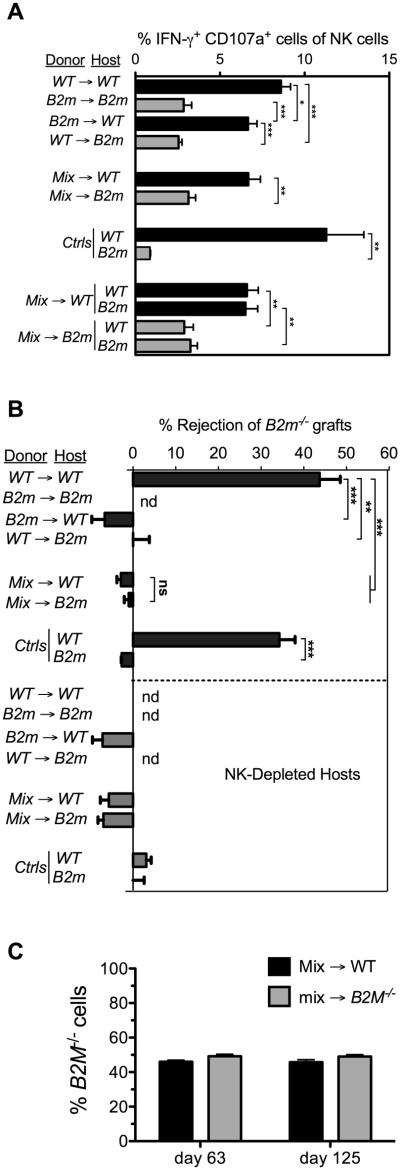
Figure 1. Responsiveness of NK cells in fetal liver chimeras to activating receptor triggering and MHC I-deficient target cells in fetal liver chimeras.
Lethally irradiated and NK-depleted hosts were reconstituted with WT, B2m−/−, or a 1:1 mix of WT and B2m−/− fetal liver cells. Black bars indicate WT hosts; gray bars indicate B2m−/− hosts. Data represent means ± SEM. (A) Responsiveness of splenic NK cells from chimeras was tested 13 weeks after reconstitution, by stimulating for 5 h with 5μg/ml of plate-bound anti-NKG2D antibody (MI6 clone). The percentages of donor NK cells co-expressing intracellular IFN-γ and surface CD107a were determined by flow cytometry. In analyzing mix→ WT and mix→B2m−/− chimeras, we gated on the congenic CD45 markers and MHC I during the analysis to determine the separate responses of WT and B2m−/− NK cells. Data are representative of 5 independent experiments performed 13-21 weeks after reconstitution. (B) Rejection of B2m−/− spleen cell grafts by chimeras 9–17 weeks after reconstitution. Rejection of CFSE-labeled B2m−/− spleen cells, mixed with internal control B6 spleen cells, was determined by flow cytometry of spleen cells 18 h after injection of the cells. Unmanipulated B6 and B2m−/− mice were tested in parallel as controls for rejection and tolerance, respectively. To establish the role of NK cells, some groups of chimeras were pretreated intraperitoneally twice (on days -2 and -1) with 200 μg PK136 (NK1.1) antibody (NK depleted) in PBS, as indicated. n = 3-4 in all groups except NK-depleted B6 controls, where n=2. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. nd=not done. (C) Chimerism was determined on the days shown by flow cytometry of PBLs stained for H-2Kb (in this experiment), or the congenic CD45 marker (in experiments not shown), 63 and 125 days following reconstitution. Statistical significance was determined with a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005).