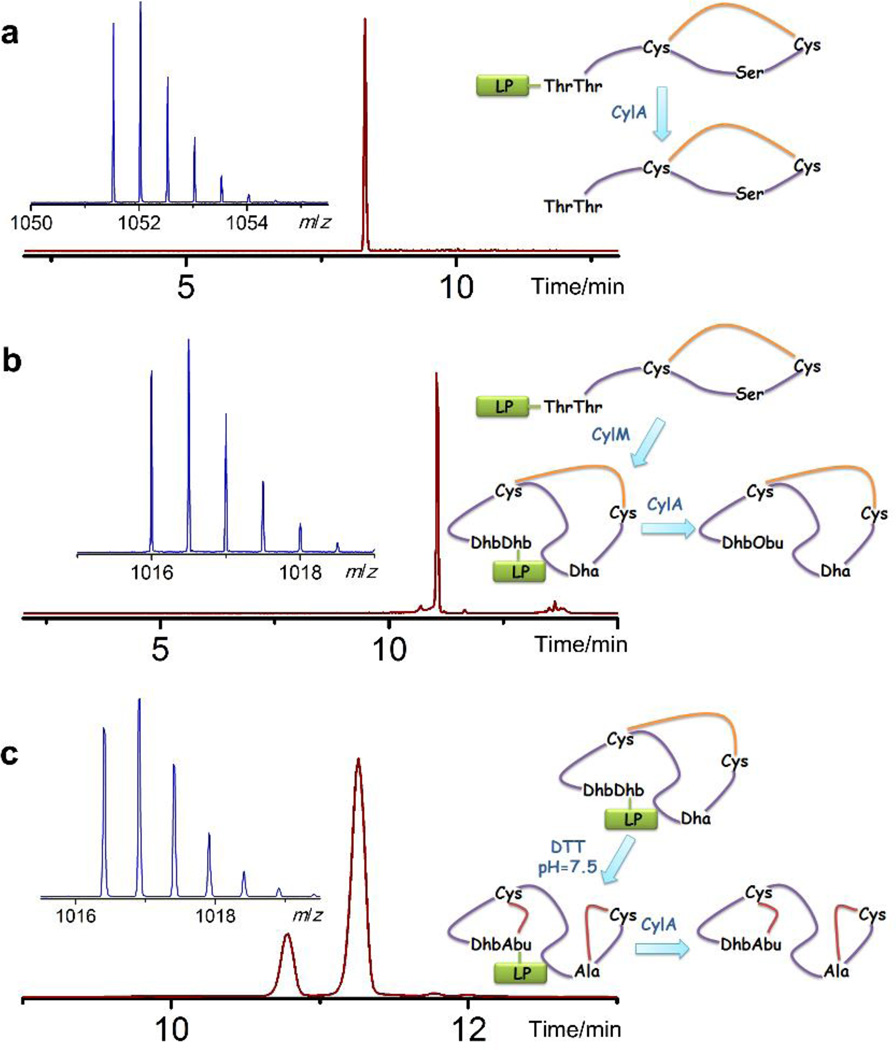
Figure 3. Non-enzymatic cyclization of cytolysin S peptide in vitro.
a) ESI LC-MS analysis of the linear core peptide of CylLS in its oxidized (disulfide) form. Extracted ion chromatogram (m/z = 1052) of the LC trace for oxidized CylLS core peptide is shown in dark red and the corresponding mass spectrum in the insert. No peak corresponding to reduced CylLS core peptide was detected in the LC trace. Oxidized CylLS core peptide with a disulfide linkage, calculated [M+2H]2+: 1,051.53, monoisotopic mass; observed [M+2H]2+: 1,051.53, monoisotopic mass. b) ESI LC-MS analysis of oxidized and dehydrated core peptide of CylLS. Extracted ion chromatogram (m/z = 1016.5) of the LC trace is shown with the corresponding mass spectrum inserted. Dhb1 was hydrolyzed to a ketone after leader peptide removal, resulting in a mass increase of 1 Da. Disulfide containing and dehydrated CylLS core peptide (Dhb hydrolyzed), calculated [M–4H2O–NH+O+2H]2+: 1,016.00, monoisotopic mass; observed [M–4H2O–NH+O+2H]2+: 1,016.00, monoisotopic mass. c) ESI LC-MS analysis of non-enzymatically cyclized CylLS core peptide. Extracted ion chromatogram (m/z = 1017) of the LC trace is shown. The mass spectrum corresponding to the major peak is shown in the insert. For fully cyclized cytolysin S, calculated [M–4H2O+2H]2+: 1,016.52, monoisotopic mass; observed [M–4H2O+2H]2+: 1,016.40, monoisotopic mass. Obu: 2-oxobutyrate, LP: leader peptide. Yellow line represents disulfide.