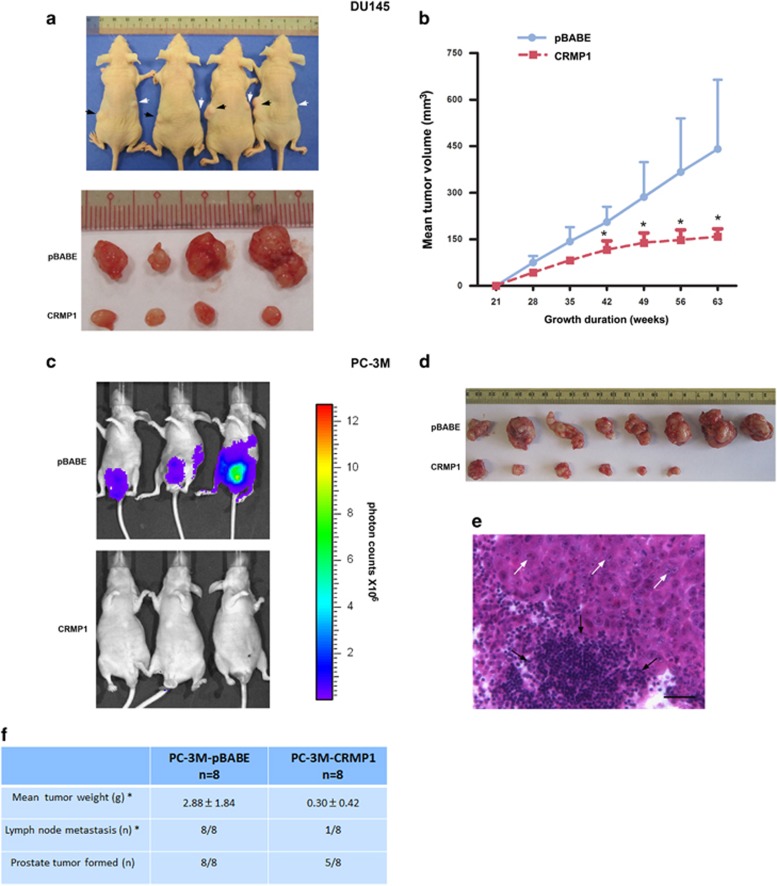
Figure 4.
CRMP1 overexpression suppresses tumorigenicity and metastasis in vivo of prostate cancer cells. (a) In vivo tumorigenicity assay. Top: Photograph shows the representative SCID mice bearing xenograft tumors formed by s.c. inoculation of DU145-CRMP1 (indicted by white arrows) and DU145-pBABE (black arrows) infectants in the same mice for comparison. Bottom: Photograph shows the dissected tumors formed by the inoculated infectants. (b) Growth curve of tumors formed by DU145 infectants in host mice for duration of 63 weeks. DU145-CRMP1 infectants formed significant smaller tumors than the DU145-pBABE infectants (n=8 for both). (c) Bioluminescence in vivo imaging. Representative bioluminescent images of mice at ninth week post-inoculation of PC-3M-CRMP1/Luc+ or PC-3M-pBABE/Luc+ cells. Significant tumor growth was detected in the prostate of mice, which received orthotopic inoculation of PC-3M-pBABE/Luc+ cells, as shown by intensive bioluminescent signals detected. However, no or barely detected weak bioluminescent signal was visualized in mice receiving inoculation of PC-3M-CRMP1/Luc+ cells. Scale bar shows the color intensity map for the bioluminescent signals expressed as photon counts. (d) Photograph shows the dissected prostate tumors formed by the inoculated CRMP1- or pBABE-transduced clones in host mice. Significant smaller tumors were formed by PC-3M-CRMP1/Luc+ clones. (e) Representative hematoxylin and eosin micrograph of aortic lymph node with prostate cancer metastasis in mouse receiving inoculation of PC-3M-pBABE/Luc+ cells. White arrows indicate the metastasizing prostate cancer cells and black arrows indicate the lymphocytes in lymph node. Magnification, × 400; bar, 50 μm. (f) Table summarizes the results of prostate tumors formed and lymph node metastasis detected in mice receiving orthotopic inoculation of PC-3M-CRMP1/Luc+ and PC-3M-pBABE/Luc+ cells. *P<0.05.