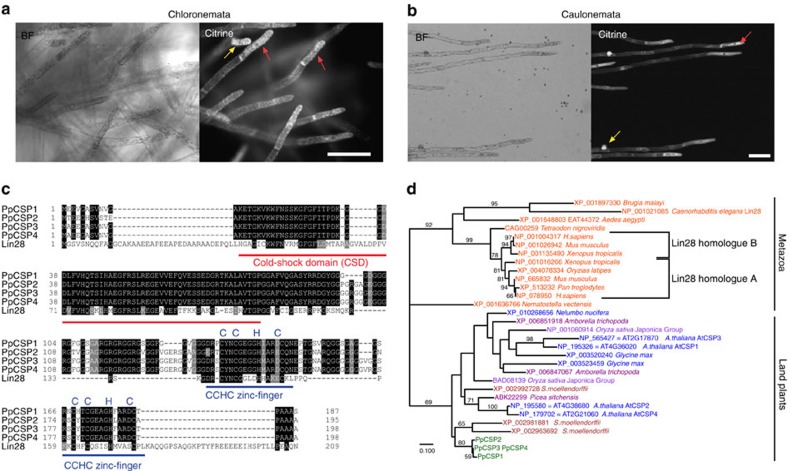
Figure 1. PpCSP1 that shares conserved domains with Lin28 is expressed in protonema apical stem cells.
(a,b) Bright-field (BF) and fluorescence (Citrine) images of chloronemata (a) and caulonemata (b) of the nPpCSP1-Citrine-nosT #136 line. Red and yellow arrows indicate apical stem cells and side branch initial cells, respectively. (c) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of PpCSPs and human Lin28 proteins. PpCSPs and human Lin28 proteins were predicted to contain one CSD (red line) and two CCHC zinc-finger domains (blue lines). Black and grey shades indicate identical amino acids and amino acids with similar characters to the consensus amino acid, respectively. (d) Phylogeny of PpCSP1, Lin28 and related proteins, with a cold-shock domain and zinc-finger domains. The maximum likelihood tree was constructed using amino acid sequences of the proteins. The wag model of amino acid substitution was used. Branch lengths are proportional to the number of substituted residues. Bootstrap probability >50% is indicated on the branches (estimated by 1,000 resampling). The accession numbers and species names are indicated. Colour of the OTU represents the phylogenetic position: Orange, metazoans; blue, eudicots; light purple, monocots; dark purple, other seed plants including gymnosperms and basal angiosperms; green, bryophytes; brown, lycophytes. This is an unrooted tree. The left-most node was chosen for the best match of organism phylogeny. Mammalian Lin28 genes used for the iPSC reprogramming are included in the ‘Lin28 homologue A'. Scale bars, 100 μm (a,b). The scale bar represents the number of amino acid substitutions per site in d.