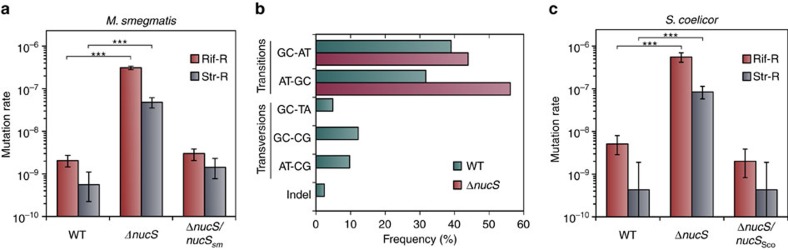
Figure 2. Mutational effects of nucS deletion.
(a) Rates of spontaneous mutations conferring rifampicin, Rif-R (red), and streptomycin resistance, Str-R (grey) of M. smegmatis mc2 155 (WT), its ΔnucS derivative and the ΔnucS strain complemented with nucS from M. smegmatis mc2 155 (nucSSm). (b) Mutational spectrum of M. smegmatis mc2 155 (green) and its ΔnucS derivative (red). Bars represent the frequency of the types of change found in rpoB. (c) Rates of spontaneous mutations conferring Rif-R (red) and Str-R (grey) of S. coelicolor A3(2) M145 (WT), its ΔnucS derivative and the ΔnucS strain complemented with the wild-type nucS from S. coelicolor (nucSSco). Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals (n=20). Asterisks denote statistical significance (Likelihood ratio test under Luria-Delbruck model, Bonferroni corrected, P value <10−4 in all cases). Mutation rate: mutations per cell per generation.