Figure 6.
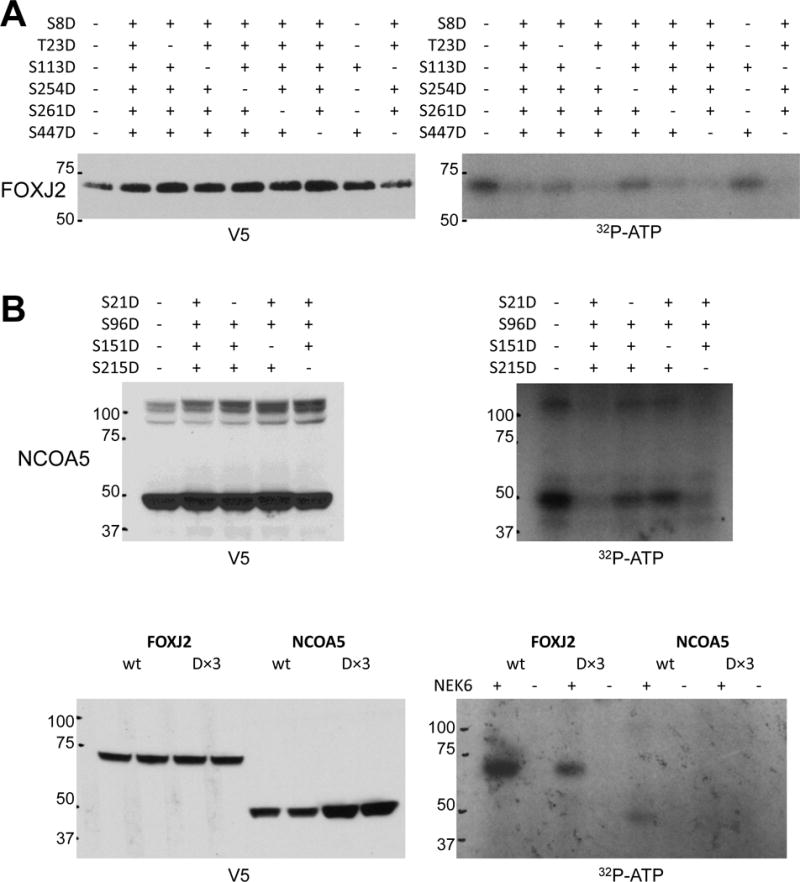
A+B. Mapping NEK6 phosphorylation sites on FOXJ2 and NCOA5. 293T cells were transfected with expression constructs for wild-type and mutant (S-to-D) versions of NCOA5 or FOXJ2 with a C-terminal V5 tag and immunoprecipitated with anti-V5 antibody; + indicates a mutation is present at that residue, − indicates that the residue is wild-type (lane 1 of each blot represents the wild-type protein). 5% of the input assayed by V5 immunoblot is shown in the left panels; the kinase assay is shown in the right panels. FOXJ2 has 10 S/T residues of the previously reported NEK6 motif L/F/W/Y-X-X-pS/pT-F/W/Y/M/L/I/V/R/K; the six residues in FOXJ2 (or homologous residues in FOXJ3) that had been previously demonstrated to be phosphorylated in phosphosite.org were assayed here. NCOA5 has 5 S/T residues in this NEK6 phosphorylation motif; however, mutating Ser201 to aspartic acid dramatically decreased exogenous NCOA5 expression, so the remaining four sites were tested in this assay. C. Kinase assay performed for wild-type and (D×3) forms of FOXJ2 and NCOA5 in the presence (+) or absence (−) of active recombinant GST-NEK6 in the assay.
