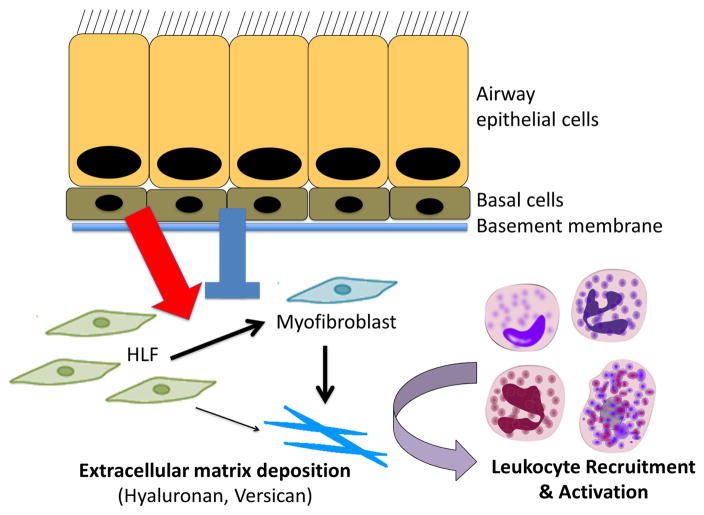
Figure 3.
Working hypothesis of leukocyte/ECM interaction in asthma suggesting that ongoing injury, irritation, and/or bacterial/viral infection of the epithelial cells results in signals that promote disordered wound repair resulting in altered ECM remodeling and the formation of a versican-/hyaluronan-rich ECM that promotes leukocyte recruitment and activation. Blue arrow indicates agonists that promote ECM accumulation and red arrow indicates antagonists the prevent ECM accumulation.