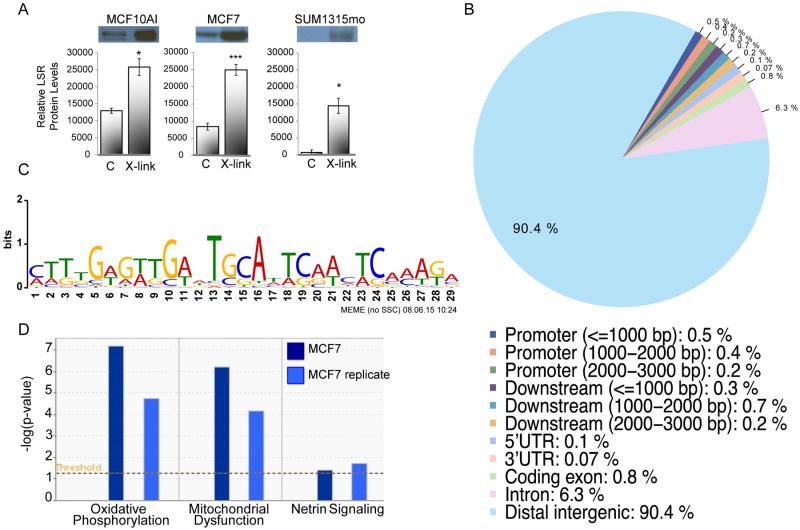
Figure 2.
LSR binds to genomic sites in breast cancer cells. A, MCF10A1, MCF7, and SUM1315mo cells were cross-linked with 1% formaldehyde (X-link), or PBS as control (C). Isolation of DNA was performed by ethanol precipitation. Detection of LSR protein was determined by western immunoblotting. Data is expressed as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001. B, ChIP-seq was performed in MCF7 cells for identification of LSR binding to genomic sites. MIME analysis of genomic sequences associated with LSR binding sites in breast cancer cells identified the LSR binding motif. C, Genomic distribution of LSR binding sites relative to genes in breast cancer cells. D, Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of three canonical pathways associated with LSR target genes.