Figure 8.
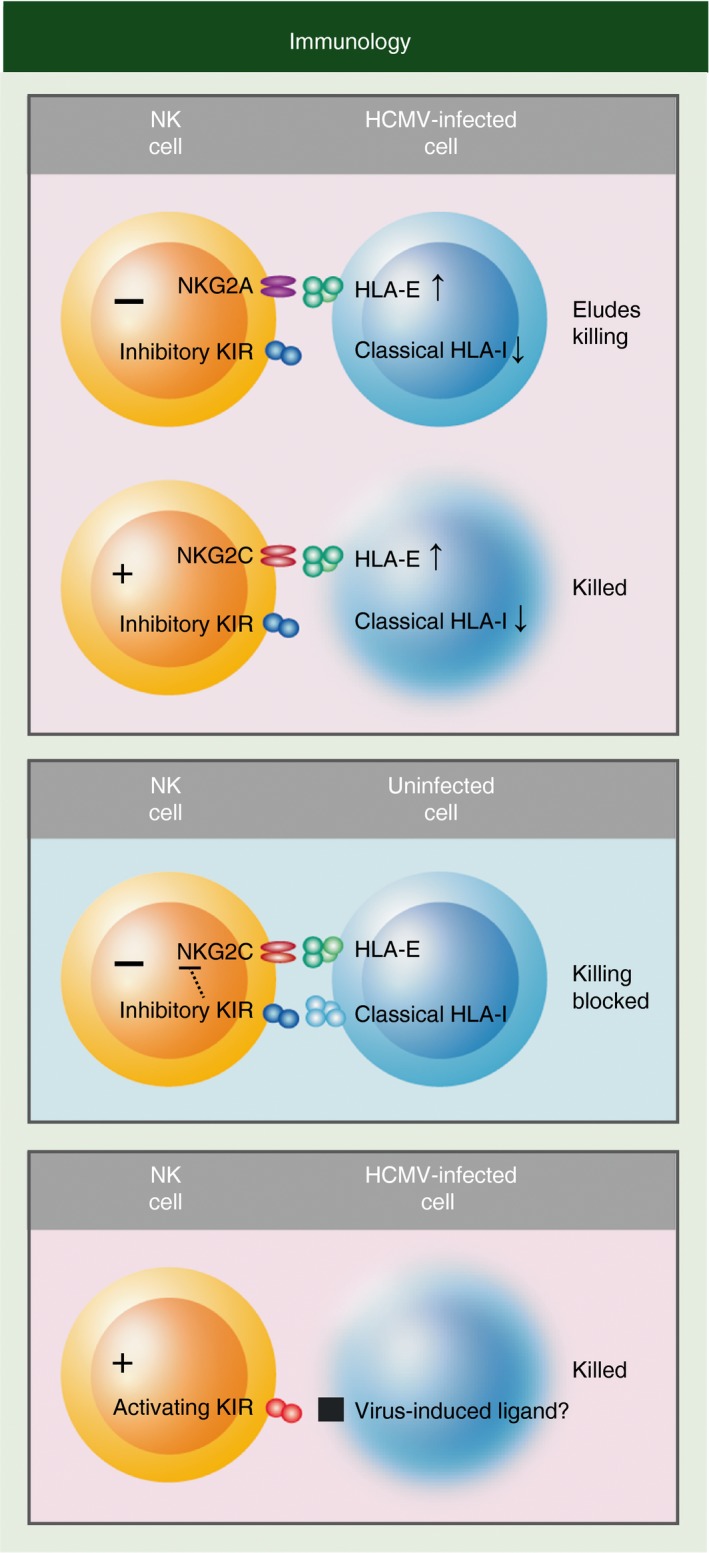
Natural killer (NK) cell strategies in human choriomeningitis virus (HCMV) infection. Viral proteins up‐regulate HLA‐E expression to selectively inhibit NK cells through the NKG2A inhibitory receptor. Concomitantly, the virus down‐regulates classical HLA class I expression to evade CD8+ T cells. NKG2C allows NK cells to detect HLA‐E+ HLA class I‐infected cells. Hence, ‘missing‐self’ (no HLA class I) triggers activation of NK cells already educated/licenced by self‐HLA class I molecules.165, 178 Non‐infected cells are protected from NK cell cytotoxicity by recognition of HLA class I by inhibitory killer‐cell immunoglobulin‐like receptors (KIR), which curbs activation through NKG2C. Activating KIR may directly recognize ‘altered‐self’ ligands that are induced by the virus.15
