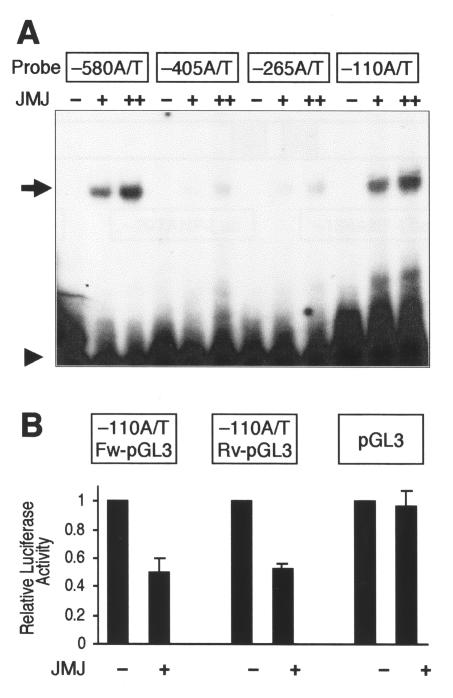
FIG. 2.
JMJ binds to DNA motifs in the ANF enhancer, which mediate repression by JMJ. (A) Representative GMSA with the six A/T-rich sequences in the −638 ANF promoter-enhancer. The 32P-end-labeled probe (20 fmol; 50,000 cpm/lane) was incubated with 20 (+) or 100 ng (++) of GST-JMJ 529-792, as indicated. The reaction mixtures were loaded onto 5% nondenatured PAGE and autoradiographed. The arrow and arrowhead indicate the probe bound to JMJ and free probe, respectively. JMJ showed stronger binding to two of the sequences (bp −580 and −110) (arrow), in a dose-dependent manner, than to other A/T-rich sequences. Sequences of the six oligonucleotides are presented in Materials and Methods. (B) JMJ represses the reporter genes containing the JMJ-binding site in the ANF enhancer. The reporter plasmids containing the −110 A/T-rich sequence selected by GMSA were constructed by subcloning the oligonucleotide into the pGL3-promoter vector in the forward (−110A/T Fw-pGL3) or reverse (−110A/T Rv-pGL3) direction. Transient transfection assays were performed by using 10T1/2 cells as described for Fig. 1B. The reporter genes (1 μg) were cotransfected with 0.5 μg of JMJ in the expression vector. Filled bars represent the means and T bars indicate the standard errors of the means for three separate transfection assays with duplicate plates.