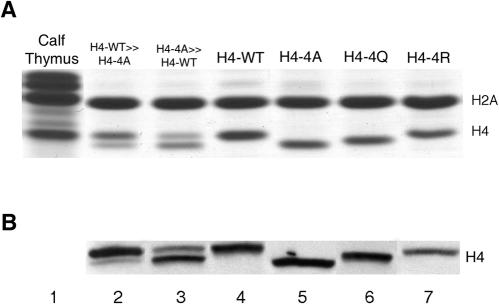
FIG. 1.
Histone H4 variant proteins can be resolved on polyacrylamide gels. (A) Coomassie-stained gel showing the different mobilities of the wild-type and mutant histone H4 proteins from the H4-WT (YJB344), H4-4A (YJB347), H4-4Q (YJB2861), and H4-4R (YJB348) strains. Nuclear extracts were prepared from exponentially growing strains and separated by reverse-phase HPLC, and fractions containing histones H2A and H4 were separated by SDS-18% PAGE. Histone H2A coelutes with H4 during HPLC and serves as a loading control (64). Lanes 2 and 3 contain mixtures of extracts from the H4-WT and H4-4A strains. Lane 2 contains approximately 75% H4-WT and 25% H4-4A, and lane 3 contains approximately 75% H4-4A and 25% H4-WT as determined by densitometry of the stained gel. (B) Western blot assay of WCEs of the same strains as in panel A separated by SDS-22% PAGE and probed with the anti-H4-17-33 antibody.