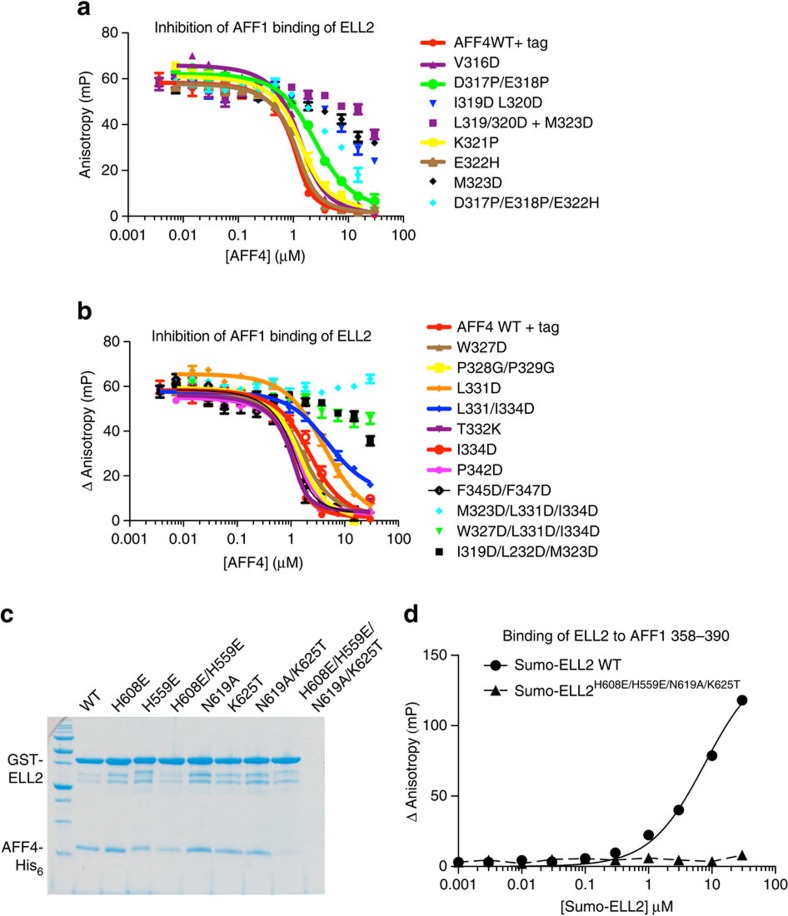
Figure 5. Contributions of AFF4 ELLBow interactions to binding in solution.
(a) Binding of AFF4ELLBow wild type (WT) and mutants in the N-terminal α-helix to Sumo-ELL2Occ. Sumo-ELL2Occ binding to fluorescently labelled AFF1ELLBow peptide 358–390 is competitively inhibited by increasing amounts of AFF4ELLBow, as described in experimental procedures. Error bars reflect the s.e. from three experimental replicates in a,b. (b) Binding of AFF4ELLBow WT and mutants in the central cluster and elbow joint, assayed as in a. (c) GST fusions of the indicated ELL2Occ mutants were immobilized and their ability to pull-down His6-tagged WT AFF4ELLBow assessed. An uncropped version of this pull-down gel is shown in Supplementary Fig. 4. (d) Direct binding of WT and mutant Sumo-ELL2 to fluorescently labelled AFF1ELLBow peptide. The assay was performed in triplicate. The s.e. from the three replicates in d is smaller than the symbols used to plot the data points.