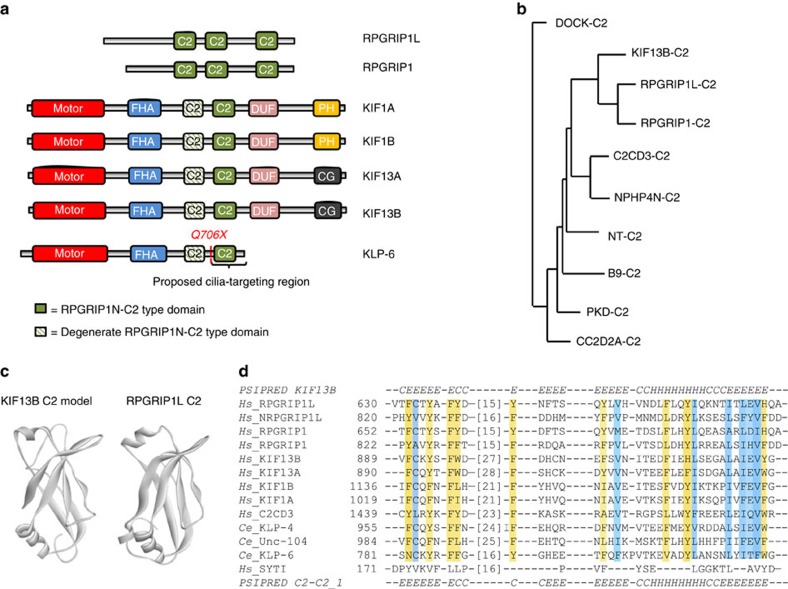
Figure 2. Identification of RPGRIP1N-C2 type domains in KIF13B and related kinesin-3 motors.
(a) Schematics of the domain structure of selected RPGRIP1N-C2 domain-containing proteins identified by bioinformatics analysis. (b) Cladogram showing the evolutionary relationship of the different C2 domain families and superfamilies. DOCK-C2, CC2D2A-C2, B9-C2, NT-C2 represent PFAM C2 superfamilies. NPHP4N-C2, human NPHP4 central C2 domain (amino acids 661-756); C2CD3, human C2CD3 C-terminal C2 domain (amino acids 1,436-1,501); RPGRIP1, human RPGRIP1 RPGRIPN-C2 type domain (amino acids 609-711); RPGRIP1L, human RPGRIP1L RPGRIP1N-C2 type domain (amino acids 588-690); KIF13B-C2, human KIF13B RPGRIP1N-C2 type domain (amino acids 861-1,000). The cladogram was reconstructed using a Neighbour Joining Using PAM250 method implemented in the Jalview program under default parameters. (c) Predicted three-dimensional structure of KIF13B-C2861-1,000 compared to the solved crystal structure of the RPGRIP1N-C2 domain in RPGRIP1L (PDB: 2YRB). (d) Alignment of selected RPGRIP1N-C2 type domains identified in our bioinformatic survey. The remote C2 domain of synaptotagmin I (SYTI) is included for comparison. The defining signature of aromatic amino acids specific to the RPGRIP1N-C2 type domains are highlighted in light orange. Homologous residues other than those found in aromatic amino acid profiles are shown in blue. Secondary structure predictions as assessed by PSIPRED are shown above (predicted for KIF13B RPGRIP1N-C2 domain) and below (predicted for RPGRIP1 RPGRIP1N-C2 domain) the alignment. H, α-helix; E, β-sheet; C, random coils.