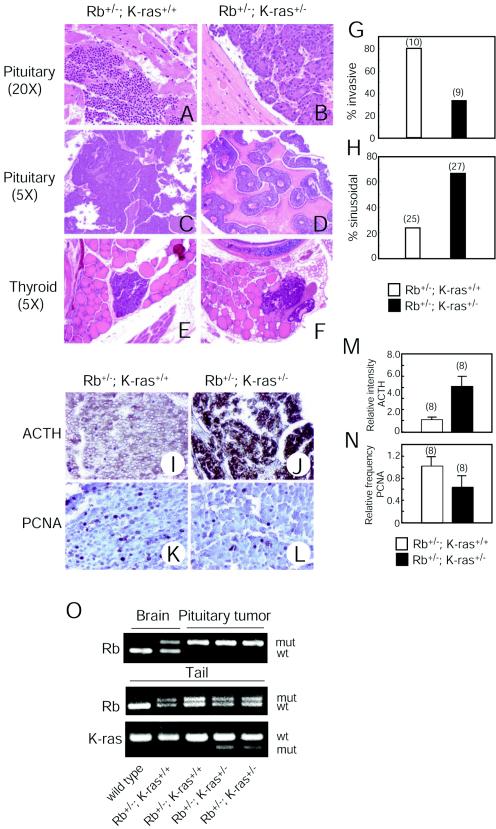
FIG. 6.
Effects of K-ras heterozygosity on characteristics of tumors arising in Rb+/− mice. (A-D) H&E-stained sections of pituitary adenocarcinomas from mice of the indicated genotypes. Magnifications, ×18 (A and B) and ×4.5 (C and D). Original magnifications are given in parentheses. (E and F) H&E-stained sections of C-cell adenomas from mice of the indicated genotypes. Magnification, ×4.5. Original magnification is given in parentheses. (G) Frequency of appearance of invasive tumors. Genotypes and numbers of mice analyzed are given. (H) Frequencyof appearance of sinusoidal (versus diffuse) pattern of growth. Genotypes and numbers of mice analyzed are given. (I and J) Anti-ACTH immunostaining of pituitary tumors arising in mice of the indicated genotypes. Magnification, ×18. (K and L) Anti-PCNA immunostaining of pituitary tumors arising in mice of the indicated genotypes. Magnification, ×36. (M) Quantification of ACTH immunostaining. Genotypes and numbers of mice analyzed are given. Bars represent means ± standard errors. (N) Quantification of PCNA immunostaining. Genotypes and numbers of mice analyzed are given. Bars represent means ± standard errors. (O) Genotyping of Rb and K-ras in normal brain tissue, pituitary tumors, and tails from mice of the indicated genotypes by PCR. The weak band for the wild-type Rb allele that appeared in one of the pituitary tumors is likely derived from nontumor cells residing in tumors. wt, wild type; mut, mutant.