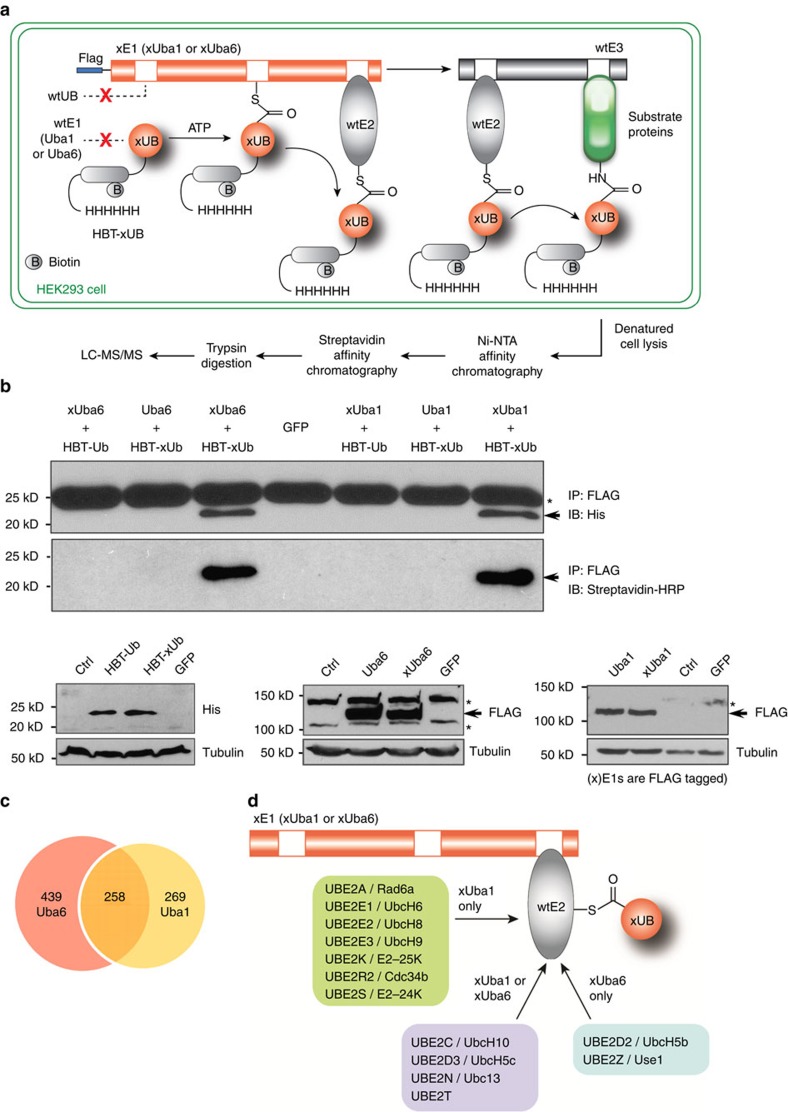
Figure 2. Profiling cellular substrates of Uba6- and Uba1-dependent ubiquitination.
(a) Flow chart of procedures to identify xUba6- and xUba1-dependent ubiquitination substrates by tandem affinity purification and proteomic procedures. (b) Specific reactions of the xUB-xUba1 pair and the xUB-xUba6 pair in HEK293 cells with lentiviral transduction. Upper panels indicate that HBT(histidine/biotinylation-signal tag)-xUB physically conjugates with FLAG-xUba6 and FLAG-xUba1, whereas HBT-wt UB shows no conjugation with FLAG-xUba6 or FLAG-xUba1. HEK293 cells were infected with recombinant lentiviruses for expression of the indicated proteins, followed by drug selection for stable integration. Conjugation of wt UB or xUB with wt E1 or xE1 proteins was examined by immunoprecipitation for E1 proteins under a non-reducing condition, followed by immunoblotting for the poly-histidine tag of UB (the upper panel) or for the biotinylation tag with streptavidin conjugated with horse radish peroxidase (HRP) (the middle panel). The arrow indicates UB proteins, while the asterisk shows a common protein around 25 kDa with cross-reactivity for the anti-penta-histidine antibody. The bottom panels demonstrate total expression levels of each protein determined by direct immunoblotting for the indicated epitope tag or tubulin as a loading control. Ctrl, parental HEK293 cells without viral transduction; GFP, cells infected with a lentivirus for green fluorescent protein. (c) Numbers of Uba6-specific, Uba1-specific and Uba6/Uba1-shared ubiquitination substrates identified by the OUT screen. (d) E2 enzymes conjugated with HBT-xUB in xUba6- or xUba1-dependent manners. The enzymes shown in the centre were identified by both xUba6- and xUba1-mediated screens.