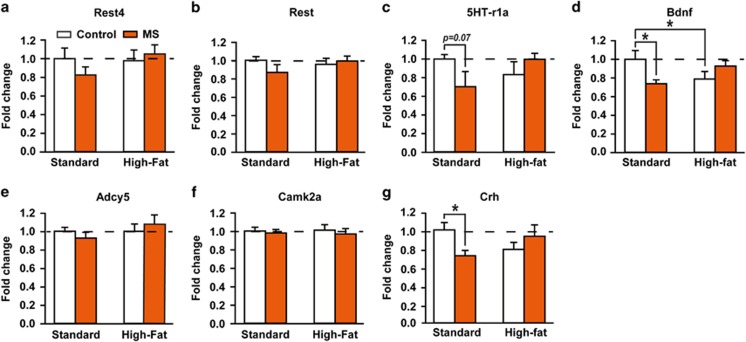
Figure 1.
Independent and combined effects of maternal high-fat diet and maternal separation on pups' prefrontal cortex gene expression. Gene expression of (a) Rest4, (b) Rest, (c) 5HT-r1a, (d) Bdnf, (e) Adcy5, (f) Camk2a and (g) Crh in the PFC of 11-day-old pups (n=10 for SD–control and HFD–control, n=7 for SD–MS and n=9 for HFD–MS; except for Camk2a: n=5 for SD–MS, n=9 for HFD–control and n=8 HFD–MS). All data are expressed relative to the housekeeping gene β2m (fold change). Pups of SD-fed dams exposed to chronic MS exhibited a slight decrease in 5HT-r1a mRNA levels, and a significant down-regulation of Bdnf and Crh mRNA. Expression of these markers was restored by maternal HFD. Adcy5, Adenylate cyclase5; Bdnf, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Camk2a, Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 2 α Crh, Corticotropin-releasing hormone; HFD, high-fat diet; MS, maternal separation; Rest, Neural-restrictive silencer element, repressor element 1 (RE1), silencing transcription factor; Rest4, Rest splicing variant 4; SD, standard diet; 5HT-r1a, Serotonin receptor 1A. *P<0.05.