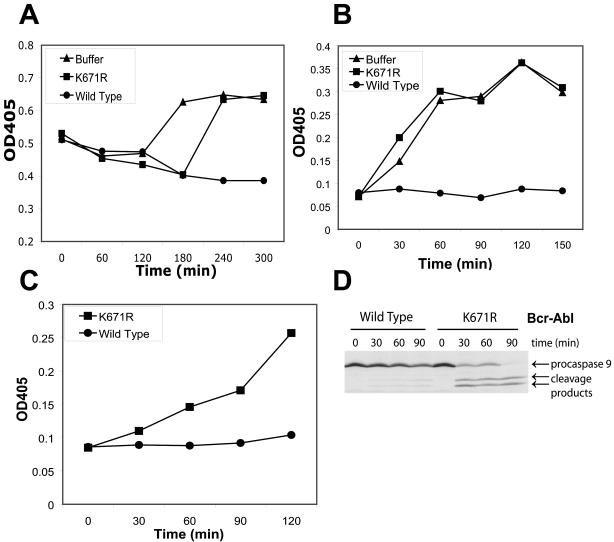
FIG. 1.
Post-cytochrome c protection by Bcr-Abl in Xenopus egg extracts. (A) Crude egg extract was incubated with buffer alone, WT Bcr-Abl, or kinase-dead (K671R) Bcr-Abl, and caspase 3 activity was measured at various time points. Caspase 3 activity was measured spectrophotometrically via cleavage of the colorimetric caspase substrate DEVD-pNA. (B) Cytosolic egg extract was pretreated for 30 min with WT Bcr-Abl, K671R Bcr-Abl, or buffer alone and then incubated with 0.6 ng of cytochrome c per μl. Caspase 3 activity was measured by cleavage of DEVD-pNA over time. (C) Cytosolic egg extract was pretreated for 30 min with WT or K671R mutant Bcr-Abl and then incubated with 0.7 ng of cytochrome c per μl for various times. Caspase 9 activity was measured spectrophotometrically by cleavage of the colorimetric caspase 9 substrate LEHD-pNA. (D) In vitro-translated, 35S-labeled procaspase 9 and soluble cytochrome c (0.6 ng/μl) were added to cytosolic egg extracts that were pretreated with WT or K671R mutant Bcr-Abl. Cleavage of procaspase 9 was assessed via autoradiography. In panels A to C, the graphs are representative of at least three independent experiments. OD405, absorbance reading at 405 nm.