Figure 5.
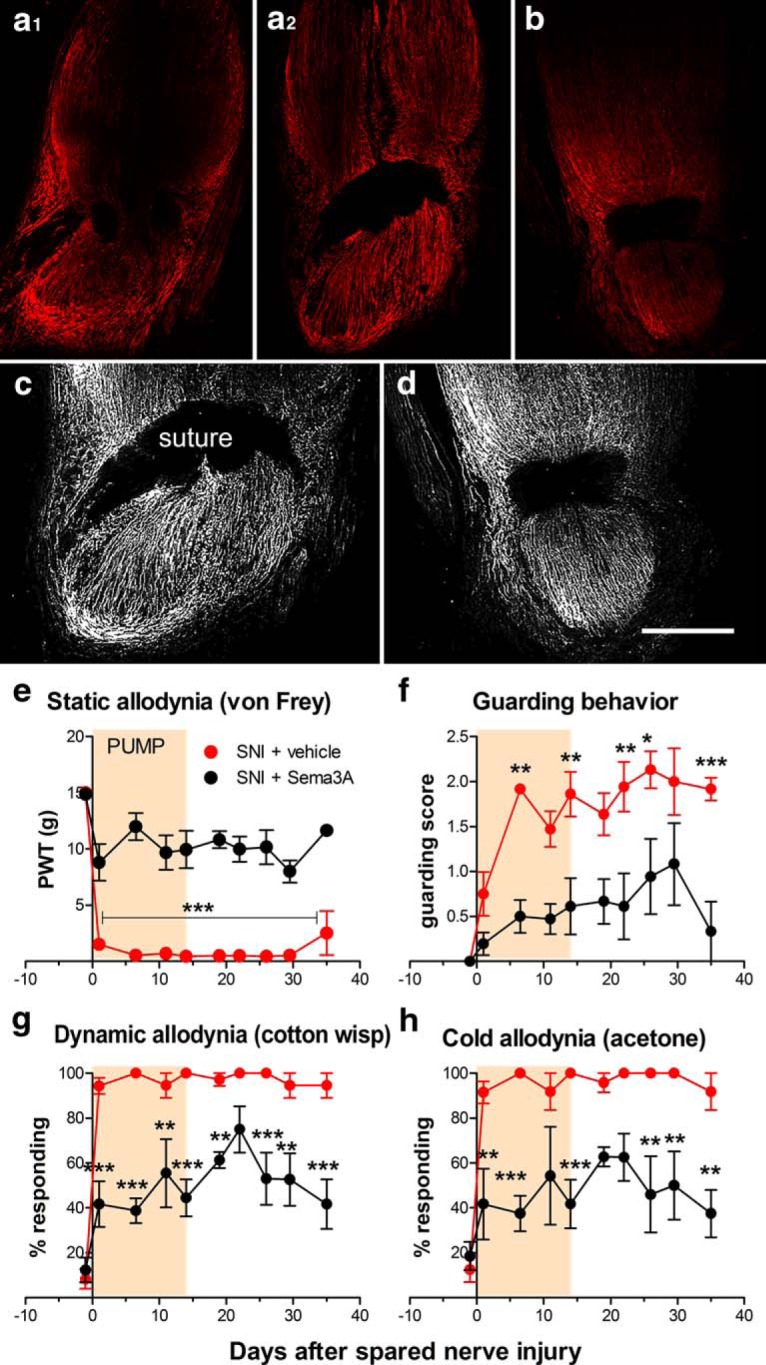
Semaphorin 3A applied to the injury site reduces regeneration and pain behavior in the SNI model. a1–b, Longitudinal sections of the neuroma region at the spared nerve injury site taken 28 d after nerve injury, stained for regeneration marker GAP43 (red). a1–b, The injury site was locally perfused with vehicle (a1, a2) or semaphorin 3A (16 µg/ml; b) for the first 14 d after the injury. a1, a2, The same nerve, taken at different depths. The suture can be seen as the two dark regions in a1 and the larger dark region in a2 and b. c, d, Grayscale rendering of portion of the images in a2 and b with sharpness enhancement to emphasize fiber structure (and to further increase the signal from b). Scale bar, 500 µm. e–h, Effect of perfusing the injury site in the spared nerve injury model with vehicle or semaphorin 3A for the first 14 d after injury on pain behaviors. e, Threshold for withdrawal responses to von Frey filaments (F(1,10) = 120.19). f, Guarding behavior score (maximum value is 3; F(1,10) = 31.33). g, Dynamic allodynia (withdrawal responses to light stroking with a fine cotton wisp; F(1,10) = 70.30). h, Cold allodynia (withdrawal responses to a drop of acetone; F(1,10) = 47.98). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, significant difference between the two groups at the indicated time points (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-test). N = 6 rats/group (4 males, 2 female). PWT, paw withdrawal threshold.
