Figure 1.
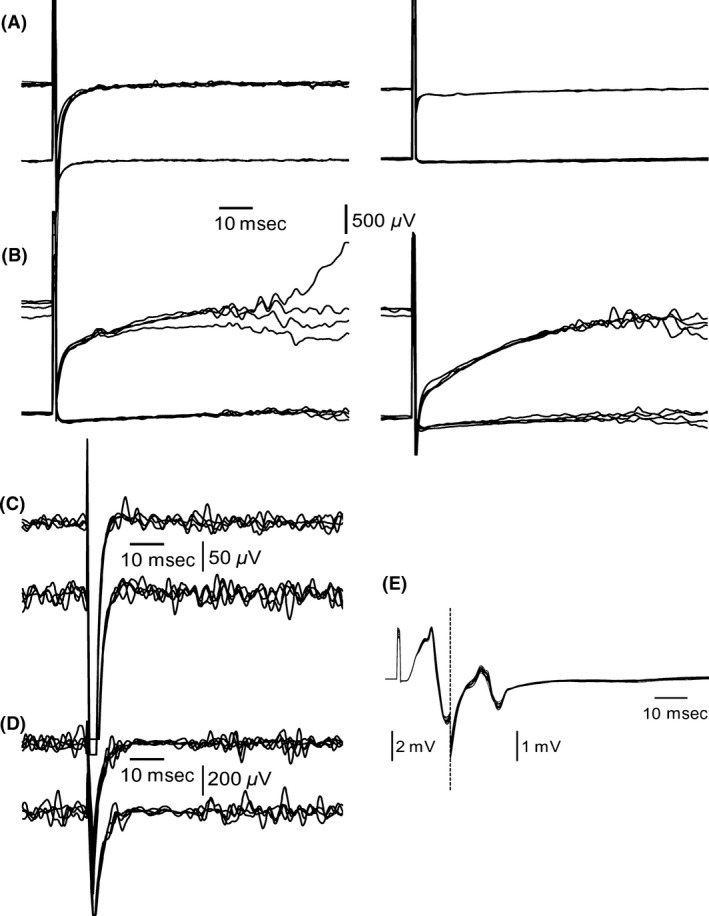
Electrophysiological findings in tetanus. (A) Blink reflex responses were lost bilaterally during the first weeks. (B) Partial recovery of the blink reflex responses occurred 11 weeks after the first symptoms. (C) Typical silent period was absent in masseter inhibitory reflex on day 3. The finding persisted for the following 9 weeks. (D) Normalization of the silent period in masseter inhibitory reflex after recovery. (E) Muscle response of the Musculus flexor digitorum superficialis on day 3 showed abnormal consistency in shape and a marked increase in amplitude.
