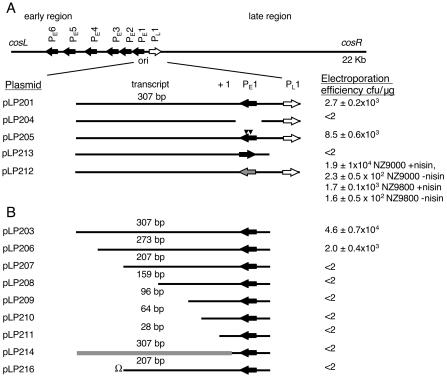
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the c2 ori locus. The positions of the origin fragment in the phage c2 genome relative to the early gene promoter (solid arrows) and the late gene promoter (open arrow) are shown at the top. Below this the c2 ori (positions 6717 to 7238 in the c2 sequence) and the derivatives of the origin fragment that were cloned in pVA891 are shown. The abilities of the various constructs (listed on the left) to replicate in L. lactis are indicated on the right as mean transformation frequencies from at least three experiments (in the case of pLP212 in the presence and in the absence of nisin); the values varied because of variations in the L. lactis transformation frequency between experiments. (A) The solid triangles indicate the position of the base pair changes in the pLP205 insert. The gray arrow represents the nisA promoter in the pLP212 insert. In pLP213 PE1 is inverted. (B) Schematic representation of c2 ori fragments cloned in pVA891 carrying shortened DNA sequences coding for the transcript made from PE1 (pLP201 to pLP211). The length of the remaining sequence of each transcript from the transcription start site is indicated above the transcript. The gray line represents the lactococcal prtP sequence replacing the c2 transcript-encoding sequence in the pLP214 insert. Ω in pLP216 represents the transcriptional and translational terminator cloned at the 3′ end of the 207-bp transcript-encoding sequence.