Figure 7. A model for the evolution of the atypical sex determination system in M. minutoides.
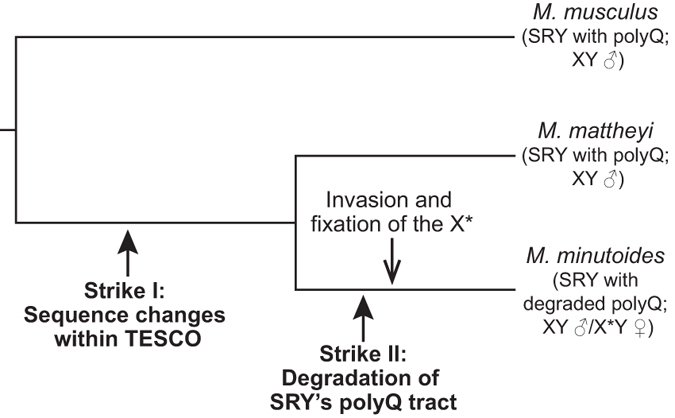
In a common ancestor to M. mattheyi and M. minutoides, multiple sequence variations within TESCO occurred. This first strike significantly reduced the basal transcriptional activity of TESCO and attenuated its response to SF1. Subsequently, a second strike hit Sry in an ancestor to M. minutoides, causing a severe degradation of its polyQ tract. Such a degenerated SRY retains only weak capacity to activate TESCO and Sox9 expression. Together, these genetic events have rendered the male sex-determining pathway vulnerable in M. minutoides, which may have facilitated the invasion and subsequent spread of the X* chromosome (and feminising modifier(s) thereon). The presence of X* chromosome in X*Y individuals overwrites the fragile male sex-determining pathway and leads to female sex reversal.
