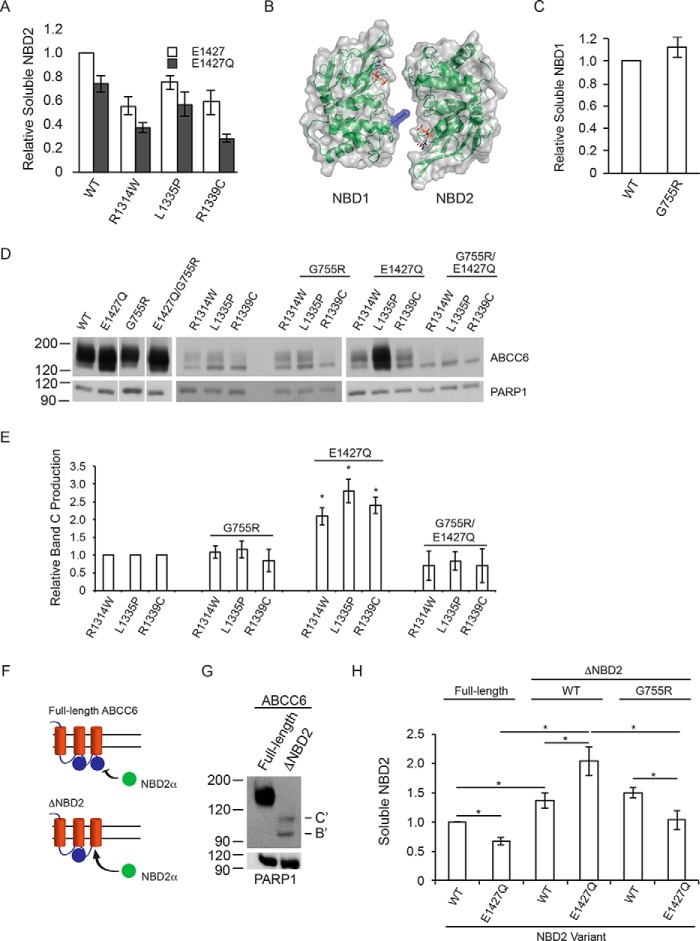
FIGURE 4.
NBD structure, dimerization, and biosynthetic correction of ABCC6. The role of NBD dimerization in the E1427Q-mediated ABCC6 rescue was assessed. A, soluble NBD2, assessed using the β-galactosidase assay is shown normalized to the wild type NBD2 signal. B, a schematic and surface representation of the ABCC6 NBD heterodimer is shown with the G755R substitution shown in blue. C, soluble NBD1 protein, measured using the β-galactosidase assay is shown normalized to wild type NBD1 signal. D, representative Western blots of the wild type, E1427Q, and G755R mutant ABCC6 proteins are shown with and without the NBD2 mutations. E, densitometric analysis of Western blots is shown for the NBD2, G755R and E1427Q mutants. F, a schematic showing the trans complementation of NBD2 co-expressed with full-length or truncated forms of ABCC6 is shown. G, a representative blot of the biosynthesis of the ΔNBD2 protein is shown. The core and glycosylated forms are indicated with B and C, respectively, with B′ and C′ indicated the core and fully glycosylated species of the truncated ABCC6 protein. H, co-expression of NBD2 with the ΔNBD2 protein is assessed by the β-galactosidase assay. Data shown are summary or representative of n ≥ 3 independent experiments. Quantified data are mean ± S.D. *, p < 0.01 using ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test.