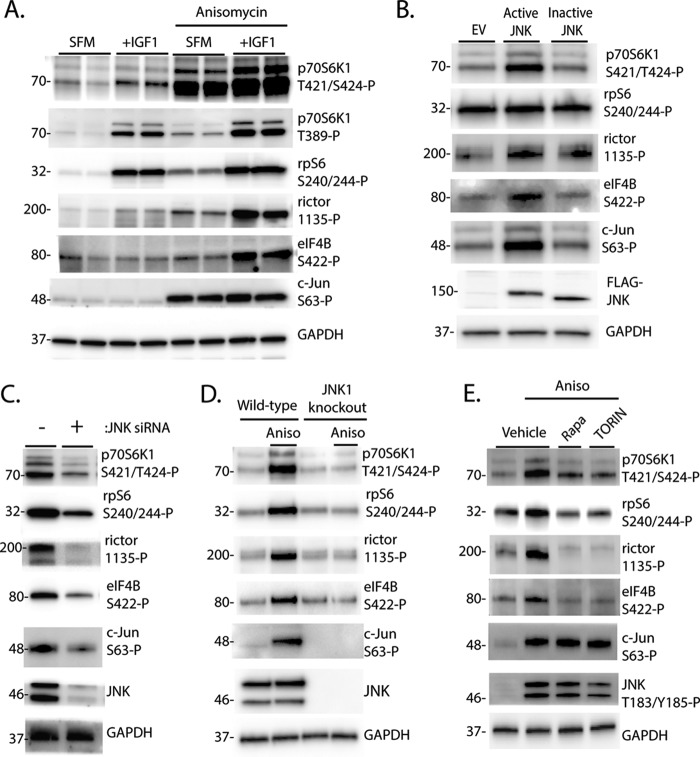
FIGURE 3.
JNK promotes p70S6K1 phosphorylation and facilitates activation of the kinase in an mTORC1-dependent manner. A and B, HEK293E cells in culture were maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and serum-deprived (SFM) for 2 h to repress phosphorylation of p70S6K1. Cells were then treated with anisomycin (20 μm) and/or IGF1 (10 ng/ml) as indicated for 30 min. B, cells were transfected with FLAG-MKK7-JNK1 (Active JNK), FLAG-MKK7-JNK1 APF variant (Inactive JNK), or an empty vector control (EV) before serum deprivation and stimulation with IGF1. C, cells were transfected with siRNA directed against JNK1/2. D, wild-type and JNK1 knock-out MEF were serum-deprived for 2 h and then treated with anisomycin (Aniso) as described previously. E, cells were serum-deprived for 2 h to repress p70S6K1 phosphorylation. During the last 30 min of serum deprivation, cells were treated with anisomycin (20 μm), rapamycin (100 nm, Rapa), TORIN2 (10 nm, TORIN), or a combination as indicated. Phosphorylation of p70S6K1 on Thr-421/Ser-424, rpS6 on Ser-240/244, rictor on Thr-1135, eIF4B on Ser-422, c-Jun on Ser-63, and JNK on Thr-183/Tyr-185 as well as expression of wild-type and FLAG-tagged JNK and actin or GAPDH were assessed by Western blotting. Blots shown in A–C, and E and D are representative of three and two experiments, respectively; within each experiment, three independent samples were analyzed. Protein molecular mass in kDa is indicated at the left of the blots.