FIGURE 1.
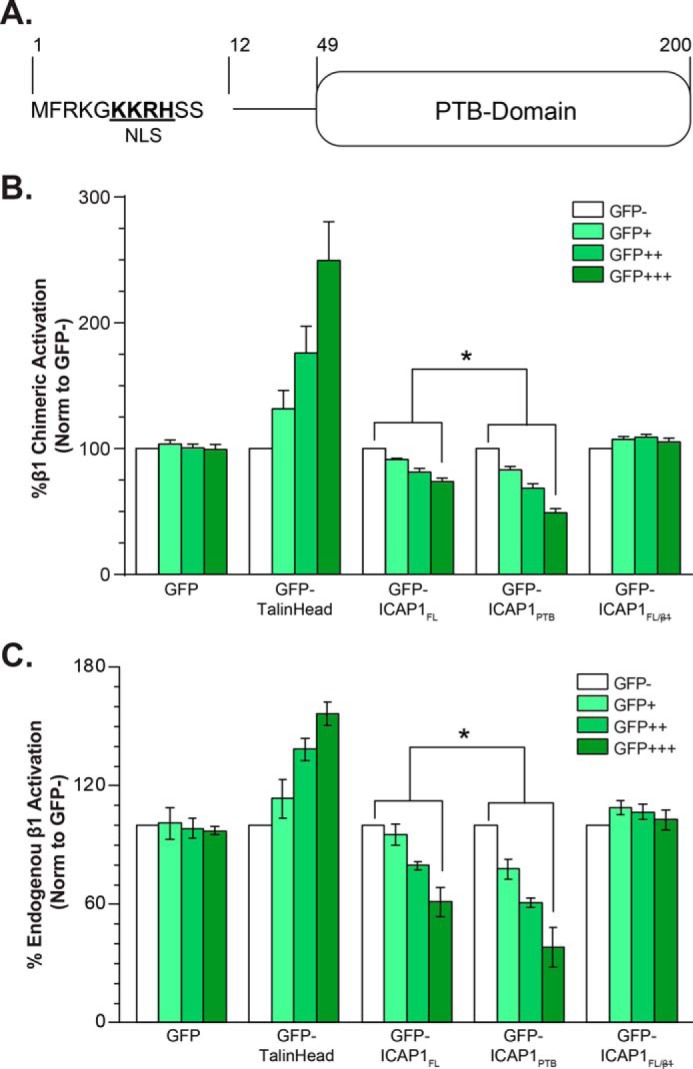
ICAP1FL is less efficient than ICAP1PTB at repressing β1 integrin activation in CHO cells. A, schematic of ICAP1 noting the NLS sequence and PTB-domain boundaries. B and C, CHO-α5β1 cells (B) or CHO cells (C) were transfected with GFP, GFP-ICAP1FL, GFP-ICAP1PTB, the integrin binding-defective mutant GFP-ICAP1FL/, or GFP-talin head, and the activation of stably expressed chimeric αIIbα5β3β1 (B) or endogenous α5β1 (C) integrins was assessed by flow cytometry. Gating on cell populations with different GFP intensities permits analysis of dose-dependent effects. The activation index of each gated population was expressed as the percentage of that in the GFP-negative population. Results are presented as mean percentage ± S.E. (error bars) of the activation index in the untransfected (GFP−) population from 4–8 independent experiments. *, p ≤ 0.01 as determined by a two-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction for multiple tests.
