FIGURE 1.
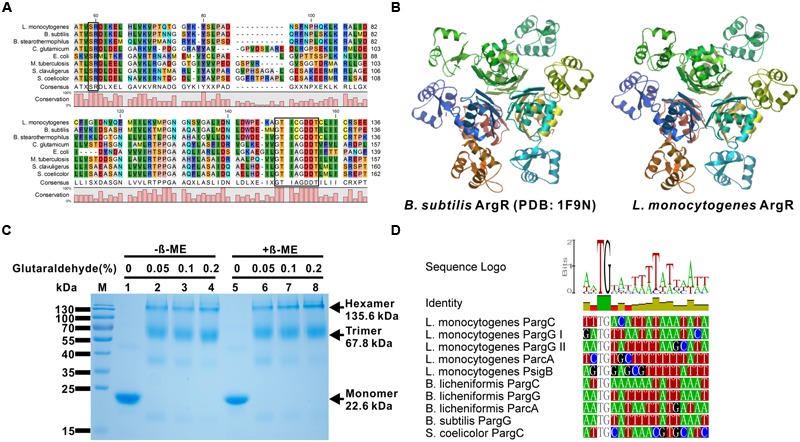
Listeria monocytogenes ArgR protein is a member of ArgR/AhrC family transcriptional regulators. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of L. monocytogenes ArgR against the members of the ArgR/AhrC family from Bacillus subtilis, B. stearothermophilus, Corynebacterium glutamicum, Escherichia coli, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Streptomyces clavuligerus, and S. coelicolor. The two conserved motifs that are responsible for DNA and arginine binding are blackened. (B) Predicted tertiary fold of L. monocytogenes ArgR using the B. subtilis ArgR (PDB: 1F9N) as the template in the SWISS-MODEL Workspace. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of glutaraldehyde crosslinking of L. monocytogenes ArgR for the identification of protein polymers. The monomeric, trimeric and hexameric proteins are indicated by arrows. (D) Promoter/operator elements containing binding sites of ArgR (ARG box) were identified by searching the L. monocytogenes genome with a position weight matrix derived from known ArgR recognition elements using the Virtual Footprint software program (as described in detail in the Materials and Methods). The identified potential consensus binding sites of ArgR in the promoter region from L. monocytogenes gene argC, argG, arcA, and sigB were further aligned with those from B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, and S. coelicolor.
