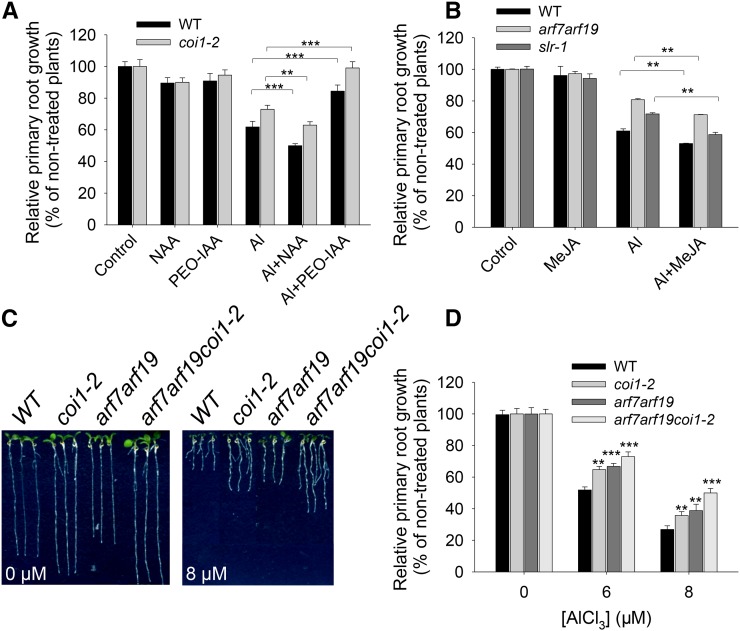
Figure 5.
The JA-mediated Al-induced root growth inhibition is independent of auxin signaling. A, Exogenous application of NAA and auxin signaling antagonist PEO-IAA affect the Al-induced inhibition of root growth at the same level in wild-type and coi1-2 mutant seedlings. The wild-type and coi1-2 mutant seedlings were exposed to 0 and 25 µm AlCl3 with or without 2.5 nm NAA or 1 µm PEO-IAA for 7 d. ** and *** indicate a significant difference between Al treatment and Al plus NAA or Al plus PEO-IAA treatment in either wild-type or coi1-2 mutant seedlings at P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively. Values represent means ± sd (n = 30). B, Exogenous application of MeJA enhanced the Al-induced root growth inhibition at the same level in wild-type, arf7arf19, and slr-1 mutant seedlings. The wild-type, arf7arf19, and slr-1 mutant seedlings were exposed to 0 and 25 µm AlCl3 in the presence or absence of 0.5 nm MeJA for 7 d. ** indicates a significant difference between Al treatment and Al plus MeJA treatment in either wild-type, arf7arf19, or slr-1 mutant seedlings at P < 0.01. Values represent means ± sd (n = 30). C and D, The root growth phenotype (C) and relative primary root growth (D) in wild-type, coi1-2, arf7arf19, and arf7arf19coi1-2 mutant seedlings in response to Al stress. The wild-type and mutant seedlings were exposed to 0 to 8 µm AlCl3 for 7 d. ** and *** indicate a significant difference between wild-type and mutant seedlings in response to Al stress at P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively. Values represent means ± sd (n = 30).