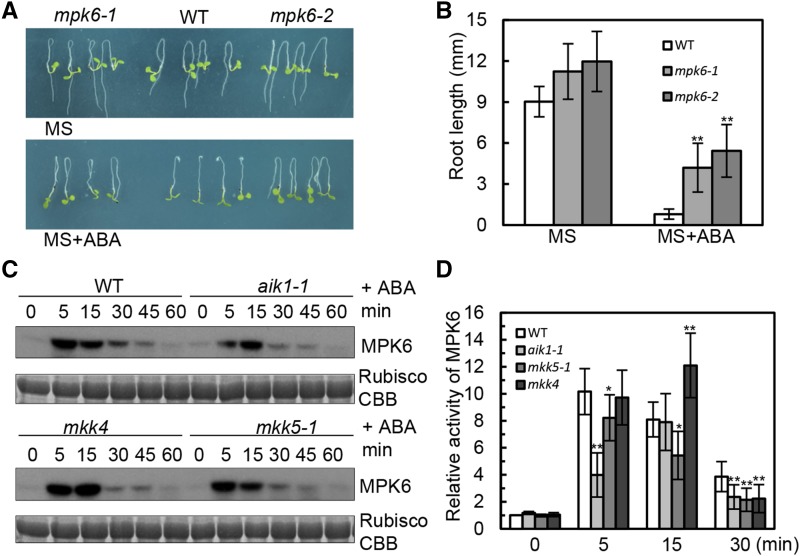
Figure 6.
AIK1 regulates ABA-inhibited root growth by activating MPK6. A and B, Five-day-old seedlings were transferred to MS medium supplemented with 50 μm ABA. Pictures were taken 3 d later. Values are the means of ∼40 seedlings. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type at **P < 0.01 by Student’s t test. C, In-gel kinase assays of wild-type, aik1, mkk4, and mkk5 plants under 100 μm ABA treatment. Equal amounts of the samples were resolved on SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB). The large subunit of Rubisco is shown as the loading control for equal protein amounts in the wild-type and mutant plants. D, MPK6 is activated by ABA. Relative MPK6 activities in the wild type, aik1-1, mkk5, and mkk4; the seedlings were exposed to 100 μm ABA. The activity of MPK6 in the wild type (0 min) was used as a control and was set as 1. Biological replications (n = 3) show the reduced activity of MPK6 in aik1-1 and mkk5 at 5 and 15 min. Error bars indicate ±sd for the different mutants. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type (0 min) at *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 by Student’s t test.