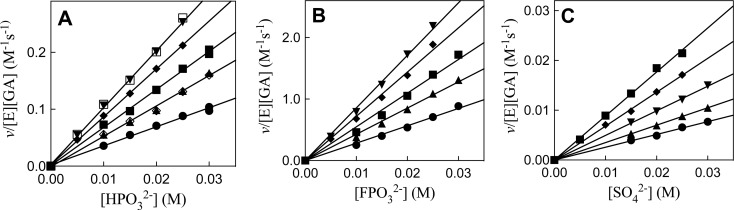
Figure 2.
Effect of inorganic dianions and Gua+ on R269A mutant hlGPDH-catalyzed reduction of GA by NADH, determined for reactions at pH 7.5, 25 °C, saturating [NADH] = 0.2 mM and I = 0.12 (NaCl). (A) The increase in v/[E][GA] (M–1 s–1), with increasing [HPO32–], for reactions in the presence of 30 mM (open symbols) or 60 mM (closed symbols) total GA [carbonyl + hydrate] and at different fixed concentrations of Gua+. The equilibrium constant for hydration of GA is Keq = [carbonyl]/[hydrate] = (6/94).8 Key: ([GA]carbonyl = 3.6 mM) (▼) 30 mM Gua+; (⧫), 25 mM Gua+; (■), 20 mM Gua+; (▲), 15 mM Gua+; (●), 10 mM Gua+; ([GA]carbonyl = 1.8 mM) (□), 30 mM Gua+; (◊), 15 mM Gua+. (B) The increase in v/[E][GA] (M–1 s–1), with increasing [FPO32–], for reactions at [GA]carbonyl = 3.6 mM and at different fixed concentrations of Gua+. Key: (▼) 30 mM Gua+; (⧫), 25 mM Gua+; (■), 20 mM Gua+; (▲), 15 mM Gua+; (●), 10 mM Gua+. (C) The increase in v/[E][GA] (M–1 s–1), with increasing [SO42–], for reactions at 3.6 mM GA and at different fixed concentrations of Gua+. Key: (▼) 30 mM Gua+; (⧫), 25 mM Gua+; (■), 20 mM Gua+; (▲), 15 mM Gua+; (●), 10 mM Gua+. Figure 3 shows the linear plots of the slopes of these linear correlations, (kcat/KGAKX)obs, against [Gua+].