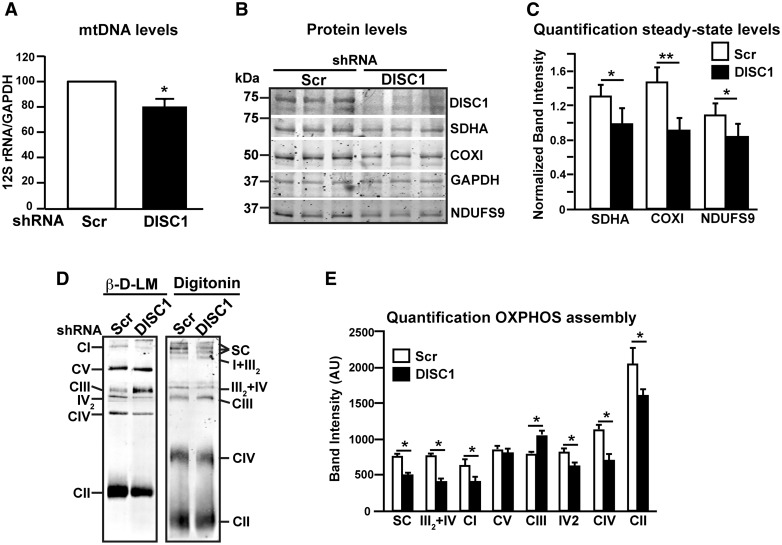
Figure 5.
hDISC1 knockdown impairs OXPHOS proteins translation and supercomplexes formation. (A) Transcription levels of mtDNA. Real-time PCR analysis of the mtDNA transcript 12S rRNA from SH-SY5Y cells stably expressing either scrambled shRNA (Scr) or hDISC1 shRNA (hDISC1). Data expressed relative to GAPDH of three independent determinations ± SD. *P < 0.05. (B) WB analysis of OXPHOS proteins showed that SH-SY5Y hDISC1 KD cells are depleted of both mtDNA and nuclear DNA encoded subunits. (C) Quantification of the steady-state levels of OXPHOS proteins. Bars represent the mean ± SD of 5 independent western blot experiments relative to GAPDH; * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01. (D) hDISC1 KD cells present partial disassembly of OXPHOS complexes and supercomplexes. BN-PAGE analysis of OXPHOS complexes and supercomplexes. Cells were solubilized either with β-D-lauryl maltoside (β-D-LM) to resolve individualized OXPHOS complexes or with digitonin to resolve OXPHOS supercomplexes. Complexes I to IV of OXPHOS were detected with an anti-NDUFS9 subunit antibody (CI), SDHA subunit antibody (CII), Core1 antibody (CIII) and COXI antibody (CIV). ATP synthase (CV) was detected with the anti-subunit β antibody. IV2, dimer of CIV detected with the COX1 antibody; SC, supercomplexes I + III2 + IVn. (E) Quantification of OXPHOS complexes and supercomplexes assembly, comparing the immunoreactive band intensities of the antibodies used in (D) between DISC1 KD cells and its Scr control cells. Bars represent the mean ± SD of 5 independent BN-PAGE experiments; * P < 0.05.