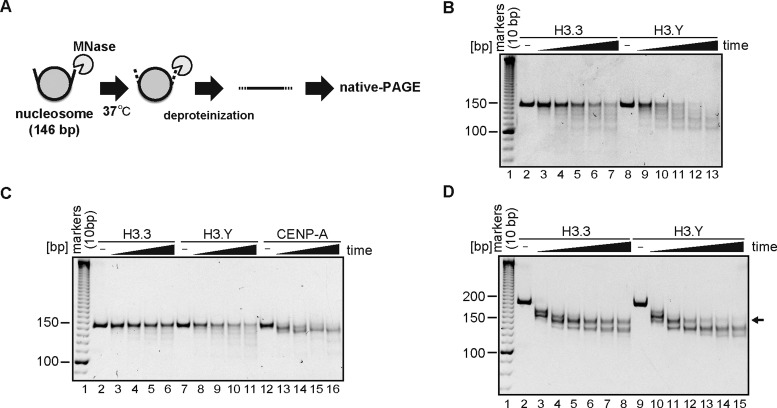
Figure 2.
DNA end flexibility of the H3.Y nucleosome. (A) Schematic representation of the MNase treatment assay. The flexible DNA ends of the nucleosome are preferentially digested by MNase. After deproteinization, the remaining DNA fragments were analyzed by non-denaturing PAGE with ethidium bromide staining. (B) MNase treatment assay. The H3.3 (lanes 2–7) or H3.Y (lanes 8–13) nucleosomes containing a 146 base-pair DNA (α-satellite derivative) were treated with MNase for 0, 3, 6, 9, 12 and 15 min at 37°C. After the incubation, the reactions were stopped by adding proteinase K solution, containing SDS and EDTA. The reaction products were analyzed by non-denaturing 6% PAGE with ethidium bromide staining. The gel image shown is a representative of four independent experiments with similar results. Other experiments are shown in Supplementary Figure S2B, C and Figure 8A. (C) The H3.3 (lanes 2–6), H3.Y (lanes 7–11) and CENP-A (lanes 12–16) nucleosomes containing a 146 base-pair DNA were treated with MNase for 0, 90, 180, 270 and 360 s at 37°C. After the incubation, the reactions were stopped by adding a proteinase K solution, containing SDS and EDTA. The reaction products were analyzed by non-denaturing 6% PAGE with ethidium bromide staining. The gel image shown is a representative of three independent experiments with similar results. (D) The H3.3 (lanes 2–8) or H3.Y (lanes 9–15) nucleosomes containing the Widom601 193 base-pair DNA were treated with MNase for 0, 3, 6, 9,12, 15 and 18 min at 37°C. After the incubation, the reactions were stopped by adding the proteinase K solution, containing SDS and EDTA. The reaction products were analyzed by non-denaturing 6% PAGE with ethidium bromide staining. The arrow indicates the bands (about 150 base-pairs) corresponding to the nucleosome core particle. The gel image shown is a representative of three independent experiments with similar results.