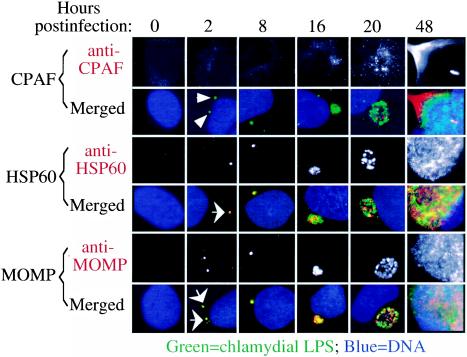
FIG. 1.
Production of CPAF in chlamydia-infected cells. HeLa cells with or without C. trachomatis serovar D organism infection at a multiplicity of infection of 1 (∼50% infection rate) were processed at various time points (in hours) after infection (as indicated on top of the figure) for triple immunofluorescence staining. DNA was labeled with Hoechst dye (blue), and chlamydial organisms were labeled with an anti-LPS MAb (green). The chlamydial antigens CPAF, HSP60, and MOMP were labeled with corresponding antibodies and are displayed both in single-color (gray) and triple-color (red) images. CPAF was not detectable until 16 h after infection. Arrowheads indicate chlamydial organisms labeled with the anti-LPS antibody alone without colocalization with CPAF while arrows indicate colocalization (yellow) of LPS and HSP60 or MOMP to the same chlamydial organisms. CPAF was secreted into the host cell cytosol at the late stages of infection while both HSP60 and MOMP remained inside chlamydial inclusions throughout the course of infection. Note that CPAF was not detected at 2 and 8 h, and CPAF was not associated with chlamydial organisms even when CPAF became detectable 16 h after infection.