Figure 8. Simultaneously tuning contractility and adhesion in an amoeboid mode migrator.
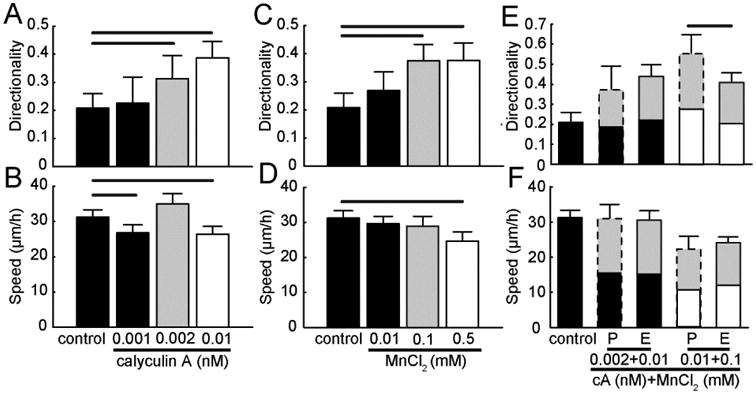
MTLn3 cells on aligned collagen fibrils in the presence of single activator (calyculin A or MnCl2) or combination of inhibitors (calyculin A and MnCl2). Migration (A) directionality and (B) speed of MTLn3 cells in the presence of only calyculin A. Migration (C) directionality and (D) speed of MTLn3 cells in the presence of only MnCl2. Migration (E) directionality and (F) speed of MTLn3 cells in the presence of both calyculin A and MnCl2. Black bars are conditions that show similar migration directionality and speed as compared to control. Grey bars are conditions that show different migration directionality, but similar migration speed as compared to control. White bars are conditions that show different migration directionality and speed as compared to control. Predicted (P) values for migration directionality and speed under dual perturbations are calculated from the single cue experiments and are marked with dashed lines. Experimental (E) values for migration directionality and speed under dual perturbations are marked with solid lines (Nexperiments ≥ 3 and Ncells per experiment ≥ 90). Error bars are 95% confidence intervals. Predicted dual perturbation 95% confidence intervals are propagated from the single perturbation experiments. Black lines indicate that the means for different conditions are statistically significant. Statistical significance was determined for p < 0.05 using two-tailed student's t-test.
