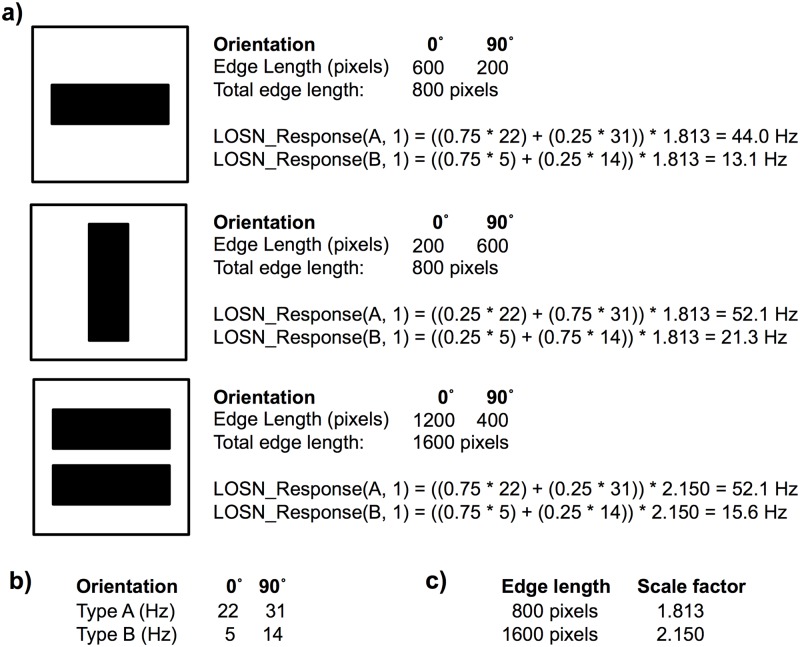
Fig 6. Worked example of LOSN calculations. Simplified example of the lobula orientation-sensitive neuron (LOSN) type A and type B firing rate response calculations.
(a) Here we calculate values for just the left dorsal eye (quadrant 1) with only horizontal (0°) and vertical (90°) edges presented. In the single horizontal bar example (top) 75% of the overall edge length is at a 0° orientation (600 pixels out of total edge length of 800 pixels) and 25% of the edges at 90° orientations, thus the LOSN responses are influenced more by the response curve values at 0° than 90°. Conversely, the vertical bar is influenced more by the response curve values at 90°, resulting in overall higher LOSN firing rates. The two horizontal bars example (bottom) has the same proportion of orientations as the single horizontal bar (top). Although the total edge length is doubled, the LOSN firing rates are not twice as high; instead they are scaled using the non-linear scaling factor derived from dragonflies (see Fig 5 and Eq 1). Note that the LOSN type A firing rate is the same for a single vertical bar as it is for two horizontal bars (52 Hz). (b) LOSN type A and type B response curve values for 0° and 90° (see Fig 5). (c) LOSN scale factors for 800 and 1600 pixel edges (See Fig 5).