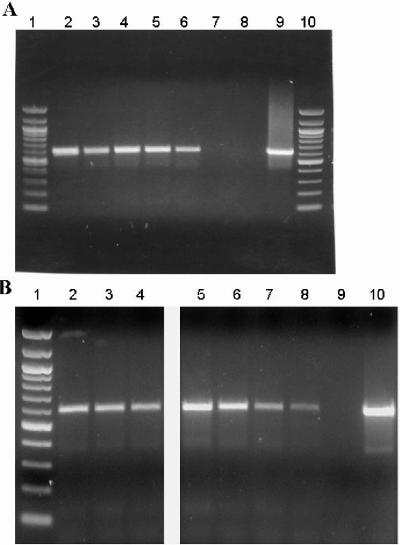
FIG. 1.
Expression of HBHA by M. tuberculosis as determined by reverse transcription-PCR analyses. (A) Total RNA extracted from the M. tuberculosis Erdman strain (lane 2), CDC1551 strain (lane 3), H37Ra strain (lane 4), or HN878 strain (lane 5) or the M. bovis BCG Pasteur strain (lane 6) or BCG Pasteur strain containing a mutation in the HBHA gene (lane 7) was reverse transcribed by using random primers and then combined with gene-specific primers designed to amplify a ∼600-bp segment of HBHA. Lanes 1 and 10 contained molecular weight markers (100-bp ladder). (B) HBHA was expressed in M. tuberculosis CDC1551 after 30 days of growth in media under normal growth conditions (lane 2), under low-oxygen conditions (lane 3), or under nutrient starvation conditions (lane 4). Similarly, HBHA was expressed in the M. tuberculosis Erdman strain in culture (lane 5), after 6 days of growth in BMMΦ in vitro (lane 6), or after 1 year of growth in the lungs (lane 7) and spleen (lane 8) of a C57BL/6 mouse. Lane 1 contained molecular weight markers (100-bp ladder). The same PCR mixture without reverse transcriptase (lane 8 in panel A and lane 9 in panel B) and the same PCR mixture containing DNA instead of RNA (lane 9 in panel A and lane 10 in panel B) were used as controls, and all cDNA preparations were shown to be free of contaminating DNA as described in Materials and Methods.