Figure 1.
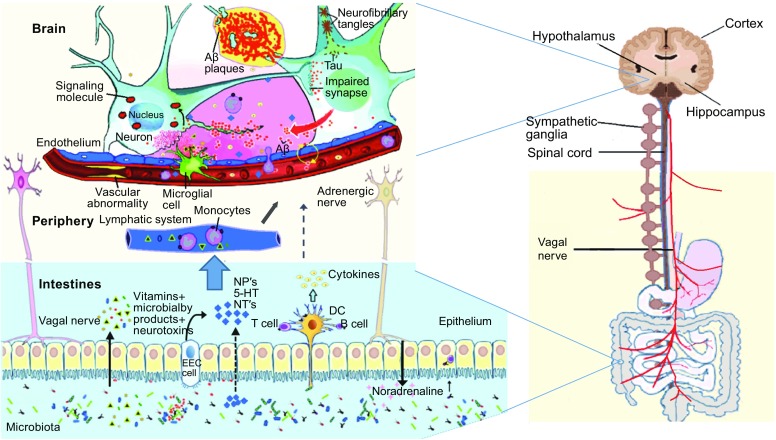
Schematic of some key players in the pathogenesis of AD. The gut microbiota regulation of neuro-inflammation and the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis activity and may lead to AD. The bacterial products that gain access to the brain through the bloodstream and the area postrema, via cytokine release from mucosal immune cells, through the release of gut hormones such as 5-HT from EEC cells, or via afferent neural pathways, including the vagal nerve. NP: Neuropeptide; NT: Neurotransmitter; 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine; DC: Dendritic cell; EEC: Enteroendocrine cell; Aβ: amyloid beta protein; AD: Alzheimer’s disease
