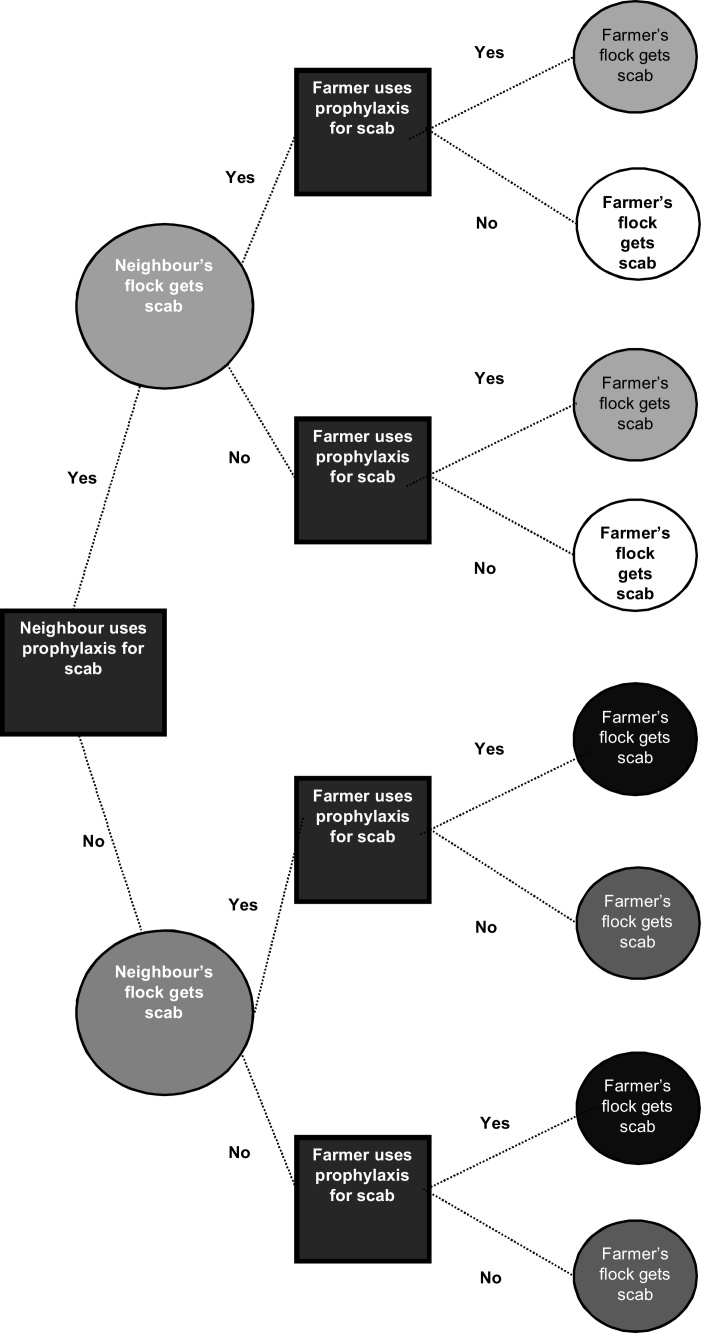
Fig. 1.
The decisions (quadrilaterals) of two farmers (Farmer and Neighbour) choosing to use or not use prophylaxis for sheep scab, and the outcomes (circles) of these decisions in a game theory model. Probability values from Table 1 were assigned to the outcomes depending on the model environment. The probability parameters of the model were then calculated as follows: Ptt- sum of small light grey circles, Pntt- sum of small white circles, Ptnt- sum of small black circles, Pntnt- sum of small dark grey circles. For each outcome where Farmer’s flock do get scab, subtracting the probability of this outcome from 1 will give the probability of an outcome where Farmer’s flock does not get scab.