Figure 1. Signaling pathway.
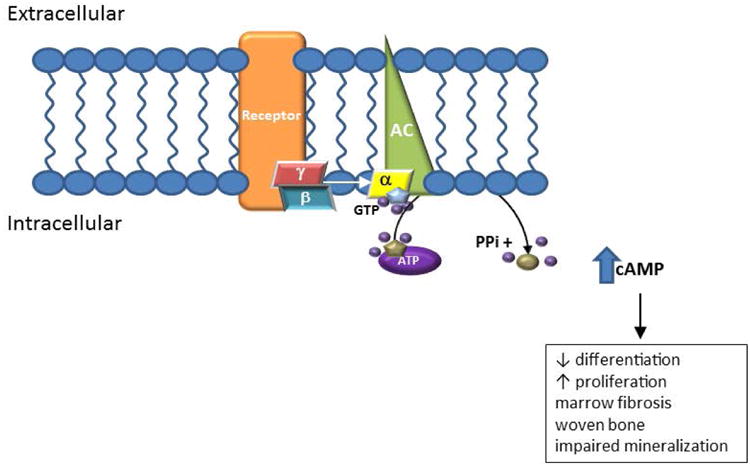
Fibrous dysplasia (FD) results from post-zygotic, activating mutations in the gene GNAS, which encodes for the Gsα subunit of the G protein complex. In FD, a mutated Gsα results in ligand-independent, continuous activation of adenylyl cyclase, resulting in excess production of intracellular cAMP. In bone, this causes proliferation of bone marrow stromal cells, leading to fibrosis, loss of hematopoiesis/marrow adipocytes, and a structurally abnormal matrix.
